Q. (a) A giant refracting telescope at an observatory has an objective lens of focal length 15m. If an eyepiece of focal length 1.0 cm is used, what is the angular magnification of the telescope?
(b)If this telescope is used to view the moon, what is the diameter of the image of the moon formed by the objective lens? The diameter of the moon is 3.48×106 m, and the radius of lunar orbit is 3.8 ×108 m.
Answer
A Focal length of the objective lens f0= 15m =15 ×102cm
Focal length of the eyepiece fe = 1.0 cm
(a) An angular magnification of a telescope is given as
Α=f0/fe
=15*102/1.0=1500
Therefore the angular magnification of the given refracting telescope is 1500.
(b) A Diameter of the moon d = 3.48×106m
The Radius of the lunar orbit r 0 = 3.8×108m
Let d' be the diameter of the image of the moon formed by the objective lens.
An angle subtended by the diameter of the moon is equal to the angle subtended by the image.
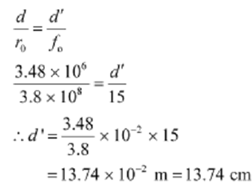
Therefore the diameter of the moon 's image formed by the objective lens is 13.74cm