What is Procambium?
The procambium produces cells that eventually become the vascular tissues xylem and phloem. These primary vascular tissues form a core in the center of the root called the stele. Steles form different patterns when viewed in cross section according to whether they are monocots or dicots. Dicot steles have xylem cells that form a cross pattern with the phloem in-between the arms of xylem. Monocots, on the other hand, have vascular tissue that forms a cylinder around a center of parenchyma cells known as the pith.
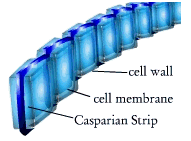
Both monocot and dicot steles are encased within a layer of cells called the endodermis. Endodermis cells actually come from the primary tissue called the ground meristem, just outside the vascular tissues, and not the procambium. This cylinder of endodermal cells is lined on the top, bottom, and their sidewalls by a waxy layer known as the Casparian Strip. The Casparian strip effectively blocks substances from moving between the walls of adjacent cells. It's as if each cell is a brick in a cylindrical brick wall, and the mortar between bricks represents the Casparian Strip. In this analogy, the Casparian Strip forms a seal that is impermeable to water and minerals, so that all materials are forced to enter the stele only through the endodermis cell membranes.
The mechanism of how roots are thought to absorb water from the soil.
Nutrients and minerals are pumped into the stele by active transport of the endodermal cells , and in this way, an osmotic gradient (high salt concentration) is maintained within the stele. Osmosis will then occur, whereby water absorbed by the root hairs flows into the stele in order to maintain osmotic balance.
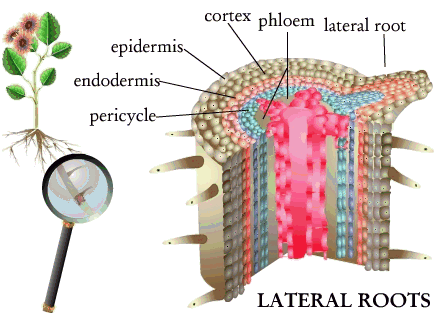
Roots do form secondary branches, and fibrous root systems form large networks of roots. Root branches are usually referred to as lateral roots because they normally form out to the sides of the main root system. Unlike shoot or stem branches, which grow from buds, lateral roots arise from within the root - in fact, within the stele. Recall that the stele is bounded by the cylindrical layer of cells known as the endodermis, and contains the vascular tissues xylem and phloem, as well as parenchyma cells that have a storage function. The stele also has meristematic cells that can start to divide by themselves. This layer of dividing cells is named the pericycle.
The pericycle cells form lateral root branches by new mitotic divisions, which produce cells that protrude into the surrounding tissue layers. These new branch cells do not puncture the endodermis, but instead keep the endodermal layer together and functioning as the endodermis expands laterally, along with the pericycle. The end result is an endodermis that remains continuous with the original primary root as it and the pericycle tissues penetrate the surrounding cells outside the stele, which are referred to as the cortex.