Q. What is Peroxodisulphuric Acid?
It is also known as perdisulphuric acid or simply persulphuric acid. The acid can be obtained by the action of chlorosulphonic acid on H202:
H2O2+ 2ClSO2 OH -----------------> H2S2O8 + 2HCl
This acid is obtained by the electrolysis of 50% sulphuric acid in cold using high current density and a platinum anode. The following reactions are supposed to take place during the process:
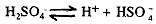
2HSO-4--------------> H2S2O8 + 2e at anode
2H+ + 2e-----------> H2
The peroxodisulphuric acid is a colourless solid, m. p. 338 K. The acid is highly soluble in water. In aqueous solution it slowly changes to peroxomonosulphuric acid.
H2S2O8 + H2O ---------------------> H2SO5 + H2O2
Potassium and ammonium peroxodisulphate are the most important salts of this acid. These are freely soluble in water. These salts are, in fact, easier to prepare than the acid and both are made on an industrial scale by anodic oxidation of the corresponding sulphates under controlled conditions.
Peroxodisulphuric acid and its salts are powerful oxidising agents. They liberate iodine from Kl slowly. This distinguishes H2S2O8 from H2 SO5 which liberates iodine immediately.
2KI + K2S2O8 ----------------------> 2K2SO2 + I2
Both fie acids are distinguished from H2, 02by their failure to react with KMnO4,.
The peroxodisulphates also oxidise ferrous salts to ferric, manganous salts to permanganates and chromic salts to dichromate in presence of a trace of silver nitrate:
2MnSO4+ 5K2S2O8 + 8H2O -------> 2KMnO4+ 4K2SO4 + 8H2SO4
Cr2 (SO4) 3+ K2S2O8 + 7H2O------> K2Cr2O7 + 7H2SO4
Some metals, e.g., copper and zinc dissolve in an aqueous solution of persulphates giving metal sulphates:
Cu + K22 O8---------> CuSo4 + K2SO4
Zn + K2S2O8---------> ZnSO4+ K2SO4