What is Obesity in biochemical or physiological risk ?
Obesity results from a complex interaction of genetic predisposition and environmental factors operating throughout an individual's lifetime. It is an important risk factor for CAD and prospective epidemiological studies have shown that excess body weight is directly related to an enhanced Cardio-vascular mortality.
Overweight individuals have a two-fold increase in the risk of developing CAD and this increased risk is related to lipid disturbances, Hypertension, and insulin resistance with glucose intolerance along with a pro-inflammatory and prothrombotic effect. Furthermore, obesity is independently associated with left ventricular hypertrophy, which in itself is a risk factor for CAD.
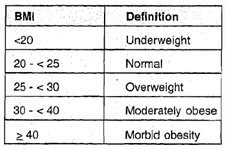
Obesity is commonly defined as 20 percentage increase in body weight over the ideal body weight. However a more precise method is to calculate the Body Mass Index (BMI) - which is the ratio of the weight in (Kg) to the height in (Metre)2.
The different grades of obesity based on BMI are as follows:
In considering obesity as a risk factor, one should understand that it is not only the, degree of obesity but also the distribution of fat that plays important role. Obesity has been defined as central (abdominal) and peripheral (hip) type depending on the place where excess fat accumulates. The former is also called 'apple' type and the latter is called 'pear' type obesity. Central or abdominal obesity with an increased intra-abdominal fat mass is more strongly associated with vascular disease than general adiposity or peripheral adiposity. The abdominal fat mass is not an inert tissue but a inetabolically active organ that produces a number of harmful substances called adipokines and is linked to insulin resistance. Visceral adipose tissue generates greater quantities of angiotensinogen, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-I), tumour necrosis factor - alpha (TNF-alpha), and resistin, and less of leptin and adinopectin. The abdominal distribution of fat has been associated with Hypertension, hypercholesterolaemia, low HDL cholesterol, hypertriglyceridaemia and elevated levels of fibrinogen - and each of these abnormalities are known risk factors for CAD.
The distribution of fat and type of obesity can be assessed by simple clinical methods like measuring the waist circumference or waist-hip ratio (WHR) in an individual. Men should have a WHR equal to or less than 0.95, whereas in women it should not be more than 0.80. The waist circumference should not be more than 90 cm in women and 100 cm in men.
While measurement of weight gives a general idea about the presence of obesity, the BMI, WHR and waist circumference are more reliable estimates of the degree of obesity and its pathologic effects. The recent INTERHEART study has shown that the WHR is the strongest anthropoinellic measure associated with risk of myocardial infarction, and is superior to BMI.