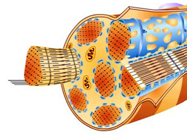
What is Muscle tissue explain briefly?
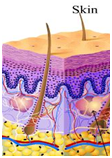
Remember that a skin cell, in addition to the genetic information that allows it to form into a skin cell, also has all of the genetic information that codes for muscle, nerve, and connective tissues, (cartilage, ligaments and tendons)! In other words, why don't skin cells also express these other genetic characteristics?
Gene control in prokaryotes is primarily involved in the response to environmental stimuli such as nutrients and environmental, or physical, factors, such as temperature, moisture, and gases. On the other hand, the primary function of genes in multicellular eukaryotes is to produce many different kinds of cells, which have specialized roles.
Current scientific understanding of gene expression in a multicellular organism holds that cells develop differently from each other because they make and build up stores of different groups of RNA (transcription) and because they synthesize different protein molecules (translation). Note that the DNA itself is not altered or lost in the process.
So, basically what happens is that different types of cells make different sets of proteins! The distinctive protein makeup or configuration of a cell then determines what kind of cell it becomes and what it does. The job of controlling the production of the protein combination falls to molecules known as gene regulatory proteins and hormones.
Control can take place at several different stages of protein synthesis, but the most common level of control is at the transcription level. Transcription, as you may recall, involves the building of a messenger RNA (mRNA) strand from the DNA template of nucleotides. Gene regulatory proteins can bind to specific DNA sequences to start the construction of an mRNA strand. This is known as a positive type of control mechanism, since it induces the production of proteins.
There are other methods of regulating the production of proteins, but these are not as prevalent as the control at the transcription level. These other controls involve stopping the transcription early on in the process, splicing mRNA molecules, cutting the RNA molecule, controlling the translation process, and the breaking down of unstable mRNA molecules.