What is Meiosis ?
Meiosis starts with a diploid cell and forms four haploid, or 1n, (or "n") germ cells. These n germ cells fuse during fertilization with another germ cell to form a diploid, or 2n cell. In higher organisms, the 2n fertilized egg becomes a zygote that develops into a new organism. The cell division steps in meiosis are similar to those in mitosis; but instead of a single division, meiosis consists of two cell divisions, meiosis I and meiosis II.
Interphase I is a period of growth and DNA synthesis, as in mitosis. In humans, the number of chromosomes doubles from 46 to 92.
Meiosis I begins with prophase I, in which the chromosomes condense and each chromosome seeks out and pairs with the homologous chromosome from the other parent cell. The two chromosomes join, or synapse, to form structures called tetrads. The term comes from the Greek word for four, because they contain four chromatids. Tetrads are also called bivalents, since they are two pairs of chromosomes.
At this stage, the chromosomes intertwine and form crosses at points called chiasmata. (The singular term is chiasma.) Crossing over, or exchange of sections of chromatids between maternal and paternal chromosomes can occur at this time, resulting in new recombinations of genetic material. Crossing over can also occur between sister chromatids. At the end of prophase I, the nuclear envelope fragments, the nucleoli disperse, and the tetrads become attached to spindle fibers by means of kinetochores.
At metaphase I, the tetrads move along spindle fibers to align themselves at the metaphase plate, with the two centromeres of each pair on opposite sides of the plate. Note that meiosis I does not pull apart the sister chromatids of any single chromosome.
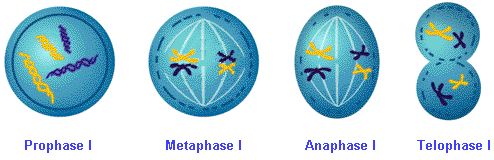
At anaphase I, the chiasmata holding homologous chromosomes together suddenly loosen. The two homologous chromosomes of each tetrad, each with two chromatids, become separated from the other pair, and each chromosome pair moves to opposite poles of the cell. Because chromosomes from each parent cell can go to either pole, or segregate independently, a second means of genetic recombination occurs. You will learn shortly in the study of Mendelian genetics that this is the basis of Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment. The number of chromosomes at each pole is half the original number.
In telophase I, the chromosomes are gathered into nuclei on each side of the cell, and the cell divides. In plants, the nuclear envelope may not re-form, and cytokinesis may not occur after meiosis I. Recall that the chromosomes at this point consist of two chromatids, each chromosome attached to its duplicate strand.
Following meiosis I, there is a short phase called interkinesis, during which the chromasomes uncoil to a greater or lesser extent depending upon the organism. In most animals, chromosomes do not uncoil after meiosis I.
Meiosis II is similar to mitosis, except that it is not preceded by DNA replication. The most important difference is that the number of chromosomes in each of the two nuclei is of a single set, rather than the double set found in mitotic divisions. Also, unlike in mitosis, sister chromatids may differ in genetic composition as a result of recombination during meiosis I.
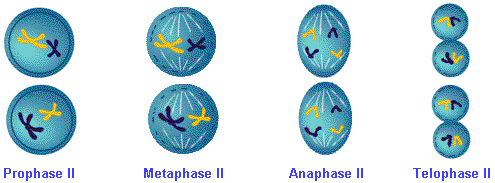
At prophase II, the chromosomes condense again, if dispersed during interkinesis, and new spindle fibers form.
At metaphase II, the chromosomes move to the metaphase plate. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids.
At anaphase II, the centromeres joining the chromatids divide and each of the sister chromatids moves to the opposite pole.
At telophase II, the chromosomes gather into nuclei and the spindle disappears, essentially reversing the events of prophase. Meiosis is complete and the cells divide.
Note that meiosis involves two cell divisions for only one replication of DNA. Because it reduces the number of chromosomes, it is often called a reduction-division.