Q. What is Gustafsons Law?
Amdahl's law is appropriate for applications where response time is significant. On the other hand there are numerous applications that necessitate that accuracy of resultant output must be high. In present situation computing power has raised considerably because of increase in number of processors connected to parallel computer. So it is probable to raise size of problem that implies workload can be raised. How does this operate? Gustafson's Law relaxed limitation of fixed size of problem as well as aimed at employing notion of constant execution time in order to conquer sequential bottleneck encountered in Amdahl's Law. This condition that doesn't suppose a fixed workload is analysed by Gustafson. So Gustafson's Law presumes the workload can increase considerably with number of processors however total execution time must remain same as highlighted in Figures below.
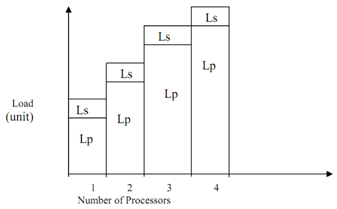
Figure: Parallel Load Increases for Gustafson's Law
As said by Gustafson's Law if number of parallel operations for a problem raises satisfactorily then sequential operations would no longer be a bottleneck. The declaration of Gustafson's law should be illustrated with help of given example. Let's discuss a problem let's say P that has to be solved with the help of a parallel computer. Let Ts be time taken that is considered as constant for executing sequential operations. Let Tp (N, L) be time taken for running parallel operations with L as whole load on a parallel computer with N processors. The complete time taken for finding solution of problem is T=Ts + Tp. Consequently S (N) can be computed as under:
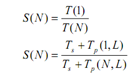
As well Tp (1, L)= N* Tp (N, L) it implies that time taken to execute parallel operations having a load of L on one processor is equal to N multiplied by time taken by one computer having N processor. If α be fraction of sequential load for a provided problem it implies that:
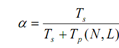
Substituting Tp (1, L) = N* Tp (N, L) we get,
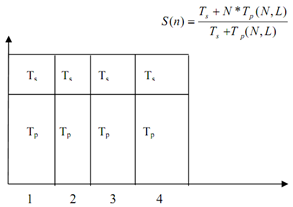
Figure: Fixed Execution Time for Gustafson's Law
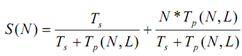
Let's change complete equation of S(N) in form of X. Now we get
S(N) = α +N * (1-α)
S(N) = N -α * (N-1)
Now let's put a number of values of α as well as compute speed up factor for rising values of α it implies that sequential factor of work load for a fixed number of processors let's say N. Figure explains a pictorial view of effect of Gustafson's Law on speed up factor. The graph illustrates as value of α rises speed up factor increases. This reduce is due to overhead caused by inter-processor communication.
Figure: S (N) vs. α αα α (Graph is not to scale)