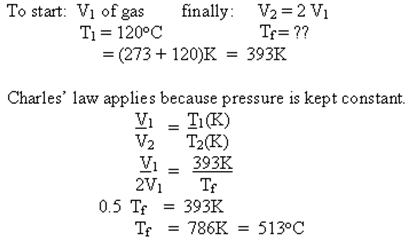What is Gas Laws?
Kinetic theory states that the speed of motion of the molecules in a substance decreases as the substance's temperature decreases. As well, the speed of motion of the molecules in a substance rises like the substance's temperature increases. If the pressure on a gas is maintain constant, adding heat to the gas will reason it to expand, or raise its volume. It was experiential that, for a given temperature change, all gases expanded by similar amount of volume. This leads to Charles' Law for gases:
V1/V2 = T1 (K) /T2 (K)
In which pressure must be constant, and as we are dealing with ratios, the volume units utilized do not matter as much as long as they match. Although, temperature should be in kelvins for this equation to work!
Kelvin extrapolated this property of gases to point out a temperature in which if the gas stayed a gas, (clearly real gases don't do this, they become liquids first) the molecules or atoms of the gas would comprise zero internal kinetic energy. Kelvin took this to be absolute zero on the temperature scale that today bears his name.
Other gas law is Boyle's Law. If the temperature is held constant, the volume of the gas changes inversely along with its pressure.
P1 V1 = P2 V2
where temperature must be held constant and pressure and volume units just need to match. These two laws can be combined to state the general gas law:
P1 V1/ T1 (K) = P2 V2/ T2 (K)
where pressure units need to match, volume units must match, and temperature must be used in kelvins.
Example - The volume of a given mass of gas will be doubled if the pressure is held constant and the temperature of the gas is increased from 120oC to what final temperature?