What is covalent bonds?
Covalent Bonds : Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons in order to become more stable. Instead of gaining electrons or losing electrons entirely, atoms share electrons, and thereby form substances with different physical and chemical properties than the component atoms. In a covalent bond, two atoms share a pair of electrons, so that each has a stable outer shell. In a double covalent bond, two pairs of electrons are shared.
For example, two hydrogen atoms are joined by covalent bonds to one oxygen atom to form water. Each hydrogen atom shares its one electron with the oxygen atom (with 6 electrons in its outer shell), filling the oxygen atom's outer shell part of the time. the oxygen atom thus becomes more stable. Each hydrogen atom, on the other hand, is able to share one of the oxygen atom's six outer shell electrons part of the time, in the process becoming more stable as well.
Covalent bonds are classified as being either polar or nonpolar, based on the distribution of the electrons being shared between the two atoms. A polar covalent bond is characterized by an uneven distribution of the electrons. The atom that is more electronegative has a greater relative attraction for electrons, causing the electrons to spend more time on it's side, or pole, of the molecule. Since the electrons are negatively charged, this produces a negatively charged pole. Conversely, the less electronegative pole of the molecule is more positively charged. This uneven electron distribution results in the molecule having two oppositely charged poles.
The water molecule is a prime example of polar covalent bonding. The electrons from each hydrogen, while shared, are strongly attracted to the oxygen atom. As a result, they spend much more time around the oxygen atom than around the hydrogen atoms. This produces an oxygen pole of the water molecule that is electrically negative, and two electrically positive hydrogen poles.
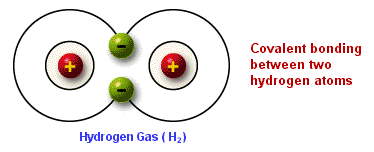
A non-polar covalent bond is characterized by an even distribution of electrons among the atoms of a molecule. Non-polar covalent bonds are present in molecules that have atoms with equal or nearly equal electronegativity. In a diatomic molecule where both atoms have equal attractions for electrons, neither atom would succeed in pulling away electrons from the other. This results in a molecule where the electrons spend equal amounts of time around the component atoms, and an absence of electrically charged poles. Examples of non-polar covalent bonds are molecules of hydrogen gas (H2), and oxygen gas (O2). Since both atoms are the same, they have equal electronegativities and attractions for electrons.