What is a Temperature Scales?
Fahrenheit, Celsius and Kelvin were scientists who studied how heat and temperature work. The most familiar scale to Americans (until the time that the USA goes thoroughly metric, don't hold your breath!) is named after the German physicist Gabriel Fahrenheit (1686 - 1736). The temperature at which pure water freezes is called 32 oF and the temperature at which pure water boils is called 212 oF. But don't blame Fahrenheit for the awkward numbers, at the time he did his experiments, he did not realize the importance of using pure water. He had some impurities like salt in the water he used to define freezing at 0oF and boiling at 200 oF. Consequently, the scale slipped away from the nice round numbers he had picked to where it is today. But it does explain why salty slush freezes when the thermometer hits 0oF or below in the winter.
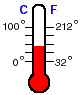
The Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius (1701 - 1744) was lucky that Fahrenheit had given it a try and shown the importance of using pure water. He assigned 0 oC to the temperature at which pure water freezes, and 100 oC to the temperature at which pure water boils. This is the scale most commonly used in laboratories today. The Fahrenheit scale is relegated to American weather reports and home thermostats, and fever thermometers.
The Fahrenheit scale divides the interval from the melting point of ice to the boiling point of water into 180oF and the same interval is covered by 100oC, so each Co is worth almost two Fo. So a change of 20Co is the same as a change of 36 Fo. The simplest way to get a good feeling for the Celsius scale, if you, like most Americans are unfamiliar with it, is to use a thermometer which has both scales side-by-side so that you can compare the Fahrenheit reading that you are used to with the Celsius reading which will be used in the laboratory. What is your normal body temperature of 98.6 oF in Celsius? What is room temperature, 65 oF, in Celsius? What is a sweltering summer temperature of 110oF in Celsius?
A further improvement in the temperature scale is called the Kelvin scale after British physicist Lord Kelvin (1824 - 1907). On this scale, 0K is assigned to the lowest possible temperature, absolute zero, where the substance has absolutely no energy to give up. Why he did this will become a bit clearer when you read about the kinetic theory of gases. Temperatures in the Kelvin scale are not measured in degrees but in kelvins, denoted by K (not by oK). On the Celsius scale, 0K corresponds to -273oC. One kelvin is the same size as one oC, so the boiling point of pure water is 373K (100oC).