After considering instruction execution let's now describe a concept which is very popular in any CPU implementation. This conception is instruction pipeline.
To extract better performance as said earlier instruction execution can be done through instruction pipeline. The instruction pipelining includes decomposing of an instruction execution to some pipeline stages. Some of the common pipeline phases can be instruction fetch (IF), instruction decode (ID), operand fetch (OF), execute (EX), store results (SR). An instruction pipe caninclude any combination of such stages. A main design decision here is that instruction stages must be of equal execution time.
A pipeline allows overlapped execution of instructions. So during the course of execution of an instruction, following can be a scenario of execution.
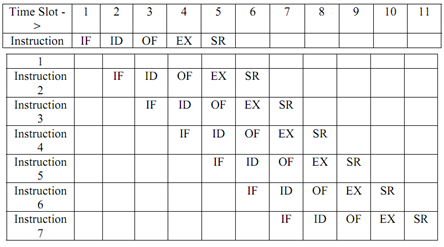
Figure: Instruction Pipeline
Please note following observations about above figure:
- Pipeline stages are just like steps. So a step of the pipeline is to be complete in a time slot. Size of the time slot will be administered by the stage taking maximum time. So if the time taken in different stages is almost similar we get the best results.
- First instruction execution is completed on completion of 5th time slot thoughsubsequently in every time slot the next instruction gets executed. Thus in ideal conditions one instruction is executed in pipeline in each time slot.
- Please note that after 5th time slot and afterwards the pipe is full. In the 5th time slot the phases of execution of five instructions are:
SR (instruction 1) (Requires memory reference),
EX (instruction 2) (No memory reference),
OF (instruction 3) (Requires memory reference),
ID (instruction 4) (No memory reference),
IF (instruction 5) (Requires memory reference),
The Pipelining Problems:
- On the 5th time slot and afterwards there can be a memory or register conflict in the instructions which are performing memory and register references that is various phases may refer to same memory/registers location. This will yield in slower execution instruction pipeline which is one of the higher number instruction has to wait till lower number instructions completed effectively pushing whole pipelining by one time slot.
- Another significant situation in Instruction Pipeline can be the branch instruction. Presume that instruction 2 is a conditional branch instruction then by the time the decision to take branch is taken (at time interval 5) three more instructions have already been fetched. So if the branch is to be taken then whole pipeline is to be emptied first. So in such cases pipeline can't run at full load.