Q. What do you mean by Frequency response?
Now let us examine the response of a circuit to a sinusoidal source, called an oscillator, whose frequency can be varied.Known as the frequency response, it is often expressed as a network function,which is an output-input ratio. In order to visualize the changes in phase shift and amplitude as the frequency of the input signal changes, a graphical display of the frequency-response characteristics of networks
is often employed.
A filter is a network used to select one range of frequencies, while rejecting all other frequencies. Let us now consider simple networks which function as filters. For the RC network shown in Figure, the voltage transfer function ¯Vout / ¯Vin is given by
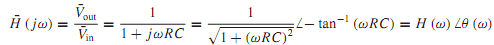
where H(ω)is the amplitude ratio and θ(ω) is the phase shift. Defining the cutoff frequency as the frequency ω at which H(ω) is reduced to 1/√2, or 0.707 of its maximum value (which is 1.0 at ω = 0), it follows that
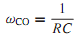
and the phase shift becomes -45° at that cutoff frequency, as shown in Figure 3.4.2. The power delivered to the circuit, at this frequency, is one-half the maximum power. As a consequence, ωCO is also called the half-power point, or half-power angular frequency.We see that this filter circuit is indeed a low-pass filter because any input signal components at ω<<ωCO are passed to the output with virtually unchanged amplitude and phase, whereas any components at ω>>ωCO have greatly reduced output amplitudes. ωCO roughly divides the passband (region of transmitted frequencies) from the stopband (region of high attenuation). The range of transmitted frequencies is known as the bandwidth. Note that in Figure 3.4.1 the low-pass filtering properties come from the fact that the capacitor is an open circuit for ω = 0 but becomes a short circuit for ω →∞ and "shorts out" any high-frequency voltage components across the output.