What are the various types of point defects? How are they caused?
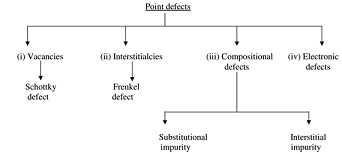
(i) Vacancies: This refers to a missing atom or a vacant atomic site because of absence of a matrix atom.
Missing of one cation and one anion ion in an ionic crystal is known as Schottky imperfection. Electrical neutrality is sustained in this type of imperfection which is observed in alkali halides.
(ii) Interstitialcies: An extra atom (substantially smaller than parent atoms) enters interstitial void or space between regularly positioned atoms. Vacancy and interestitialcy are, hence inverse phenomena.
Displacement of cation ions from a lattice site into the void space is known as Frankel imperfection and this results in creation of vacancy. An imperfection don't affect the overall electrical neutrality of the crystal.
Compositional defect:
(iii) Substitutional impurity: Presence of foreign atom in place of a matric atom is known as substitutional impurity.
If a foreign atom occupies a vacant position within crystal lattice, this defect is known as interstitial impurity.
(iv) Electronic defects: Errors in charge distribution in solids are termed as electronic defects. There is departure from the normal regularity of charge distribution. This effect is responsible for the operation of p-n junction and transistors.
Point defects formed by
(i) Thermal fluctuations during preparation of crystals.
(ii) Quenching (quick cooling) from a higher temperature
(iii) Severe deformation such as hammering or rolling.
(iv) External bombardment by atoms or high energy particles( for example Cyclotron of nuclear reactor).