What are the risk factors for the development of food allergy?
Having gone through the discussion above, can you identify at least one important factor leading to food allergy? Yes, a genuine food allergy occurs when a specific immune reaction occurs in the body in response to consuming a particular food. In other words, exposure to a food (antigen) or some element in the food (allergen, usually a protein) is a prerequisite for the development of food allergy. Excessive exposure to a particular food -for example, in Japan where rice is a staple, rice is a common food allergen; in Scandinavia the common allergen is codfish; while in India, it is chickpeas. Eggs, cow's milk, peanuts, wheat, soya and fish cause most of the allergic reactions in children. Peanuts, walnuts or almonds, fish, and shellfish (such as shrimps, crab fish, lobsters, crab) cause most of the allergic reactions in adults. Besides food allergens, other risk factors include heredity, gastrointestinal permeability, and environmental factors as highlighted in Figure. Heredity is thought to play a major role in the development of atopic disease. Atopy refers to an individual being prone to develop allergies because of a genetic state of hyper responsiveness to allergens. In most cases, allergies occur when an individual who has a genetic sensitivity to certain allergens is exposed to the substance. Family history of allergies increases our risk of developing allergies, including food allergies.
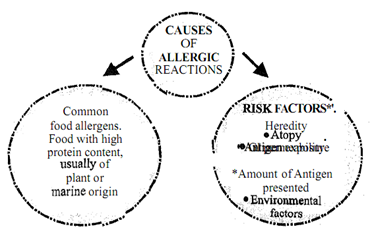
Gastrointestinal permeability may allow antigen penetration and presentation to the lymphocytes. Gastrointestinal permeability is greatest in early infancy and declines with intestinal maturation. Other conditions such as gastrointestinal disease, malnutrition, prematurity and immunodeficiency states may also be associated with increased permeability and risk of developing food allergies. Environmental factors include early exposure to microbes, tobacco smoke, exercise and cold. It is important to note that allergies are most likely to affect babies and young children because of their underdeveloped immune system.