What are the characteristics of digital ICs used to compute their performance?
Ans:
Characteristics of Digital Integrated Circuits
1. Speed of operation: The Speed of operation of a digital circuit is given in terms of the propagation delay time. The input delay times and output delay times can be demonstrated as:
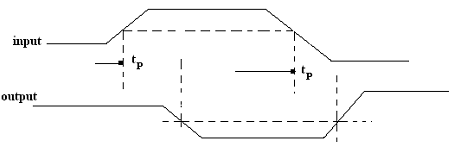
The delay times are measured in between the 50% voltage levels of input and output wave forms. Here two delay times those are t
phl, while the output goes from the high state to low state and tphl, while output goes from low state to high state.
2. Power Dissipation: It is the amount of power dissipated in an IC. It is determined through the current, ICC that this draws from the Vcc supply and is provided by Vcc x Icc. Icc is the av value of ICC [O] and ICC [1]. This is specified in mW.
3. Figure of merit: For digital IC, this is explained as the product of speed and power. This is specified in Pico joules i.e. ns x mw= pj. The low value of speed power product is required.
4. Fan Out: It is the no of the same gates that can be driven by a gate. High fan out is beneficial, as this reduces the requirement for additional drivers to drive more gates.
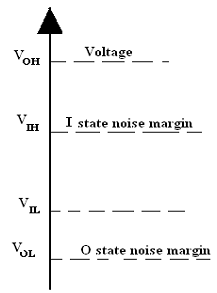
5. Noise Immunity: Stray electric and magnetic fields make unnecessary voltages termed as noise, on the connecting wires in between logic circuits. It may cause the voltage at the input to a logic circuit to drop below Vih or fuse above Vil and may generate unwanted operation. The circuit's capability to tolerate noise signals is termed to as the noise immunity.
6. Operating Temperature: A range of temperature wherein an IC functions properly should be identified. The accepted temperature range for consumer IC' s are from 0 to 70 degree C and for industrial applications [from -55° C to +125° C for military applications].