What are Possessive Pronouns and Pronominal Adjectives?
What are possessive pronouns?
Possessive pronouns are personal pronouns that serve two purposes in the sentence. They replace a noun, and they show ownership of the noun replaced.
A possessive pronoun can serve as a subject, predicate nominative, direct object, indirect object, or object of a preposition.
The possessive pronouns are as follows:
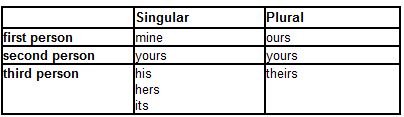
Notice that there is no apostrophe in the spelling of any of the possessive pronouns.
Pronominal adjectives (also known as possessive adjectives)
Possessive adjectives are closely related to possessive pronouns. They function as adjectives to modify the noun following them. Since they look like pronouns, many people consider them to be part of the group of possessive pronouns. Since they function as adjectives, they are more properly considered as adjectives. To satisfy both points of view we will call them pronominal adjectives (pronoun-like adjectives).
The pronominal adjectives are as follows:
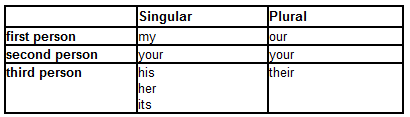
How to tell possessive pronouns from possessive adjectives
Notice that some of these pronominal adjectives look the same as the possessive pronouns. To determine if the sentence contains a possessive pronoun or a pronominal adjective, determine the function of the word in the sentence. If it used to indicate who owns a noun and the noun is present, then it is a pronominal adjective. If it indicates who owns something and also takes the place of the noun owned, it is a possessive pronoun.
Examples
1. We were forced to take his dog to the veterinarian.
"His" is a pronominal adjective because it modifies the noun "dog."
2. We were forced to take his with us.
"His" is a possessive pronoun because it takes the place of both the owner of the item and the name of the item itself. You can see that it is necessary to have clearly stated, prior to this sentence, exactly to what "his" refers. The original noun that the pronoun replaces is called the antecedent.