Weight Training Calculations -Artificial intelligence:
Because we have more weights in our network than in perceptrons, first we have to introduce the notation: wij to denote the weight between unit i and unit j. As with perceptrons, we will calculate a value Δij to add up to each weight in the network afterwards an example has been tried. To calculate the weight changes for a specific example, E, first we begin with the information regarding how the network would perform for E. That's, we write down the target values ti(E) that each output unit Oi would produce for E. Note that, for categorization problems, ti(E) will be 0 for all the output units except 1, which is the unit associated with the right categorisation for E. For that unit, ti(E) will be 1.
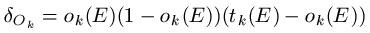
Next, example E is propagated through the network so we may record all the observed values oi(E) for the output nodes Oi. At the same time, we record all the calculated values hi (E) for the hidden nodes. For each output unit Ok, then, we calculate its error term as follows:
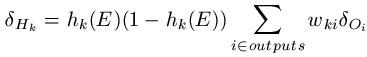
The error terms from the output units are utilized to calculate error terms for the hidden units. In actual fact, this method gets its name because we propagate this information backwards through the network. For each hidden unit Hk, we calculate the error term in following manner:
In English language, this means that we take the error term for the entire output unit and multiply it by the weight from hidden unit Hk to the output unit. Then we add all these together and multiply the sum by hk(E)*(1 - hk(E)).
Having calculated all the error values connected with each unit (hidden and output), now we may transfer this information into the weight changes Δij between units i and j. The calculation is as following: for weights wij between input unit Ii and hidden unit Hj, we add on:
[Remembering that xi is the input to the i-th input node i.e. E; that η is a small value known as the learning rate and that δHj is the error value we calculated for hidden node Hj utilizing the formula above].
For weights wij among hidden unit Hi and output unit Oj, we add on:
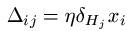
[Remembering that hi (E) is the output from hidden node Hi when example E is propagated through the network and that δOj is the error value we calculated for output node Oj utilizing the formula above].
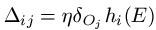
Each alteration Δ is added to the weights and this concludes the calculation i.e. E. The next instance is then used to tweak the weights further. As with perceptrons, the learning speed is used to ensure that the weights are just moved a small distance for each particular example, so that the training for earlier examples is not lost. Note down that the mathematical derivation for the above calculations is based on derivative of σ that we discussed above. For total description of this, see chapter 4 of Tom Mitchell's book "Machine Learning".