Visible and Invisible Radiation:
Light is very much a part of our existence. Without it we cannot see; It Iends colour to the world around us. Light is also termed as visible radiation. There are other kinds of radiations in nature, that we cannot see.'~hese are termed invisible radiations. Some examples of invisible radiations are the infrared and ultravioler radiations, radiowaves, X-rays and gamma rays. We may c6me across all these radiations in our lives. For example, infrared (IR) radiation is given out by warm objects, such as our bodies, room heaters, buildings and the Earth after a warm day. Rattlesnakes dctcct infrared radiation very well. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation can kill germs. It is invisible'to us but can be detected by bumblebees. Radiowaves are.emitted by TV and radio broadcasting stations and are received by our TV or radio sets through the antennas. Thus, they are useful in communication.
They can also be detected by bats. X-rays are used in medicine, gamma rays aie us in cancer treatment and are also emitted in nuclear explosions. All these radiations-the gamma ray, the X-rays, ultraviolet rays, light, infrared rays, and radiowaves-are useful in astronomy. Actually they are different forms of the sanlekind of radiation called the electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy. There are other forms of energy with which you must be familiar, like heat, sound or the energy stored in thespring of a watch. We usually think of electromagnetic radiation as being made up of waves that travel with the speed of light in vacuum. Now, the simplest examples of waves that you may know are waves of water in a pond or sea, waves on a string. You may have seen waves on a curtain fluttering in the air. Some people have wavy hair. We will not go here into the details owhat waves are, or the special nature of electromagnetic waves. For details, you may like to refer to the books listed at the end of the block. But clearly, from their description given above, the various kinds of electromagnetic radiation do not seem to be alike. What is the difference between each of them?
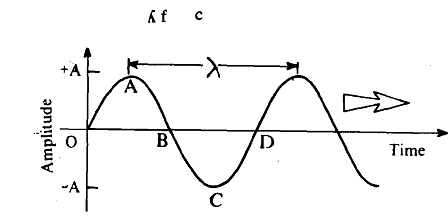
(hills) or two successive troughs (valleys) is defined as its wavelength. It is measured inmetres. The curve marked OABCD is called one cycle. The frequency of a wave is defined as the number of cycles it travels in a second. It is then measured in terms of cycles per second (cps) or Hertz. The product of the wavelength A and the frequency f of an electromagnetic wave is equal to its speed c: