Vector Form of the Equation of a Line
We have,
→r =→r0 + t→v = (x0,y0,z0) + t (a, b, c)
This is known as the vector form of the equation of a line. The lone part of this equation that is not known is the t. Note that tv→ will be a vector which lies along with the line and it tells us how far from the original point that we have to move. If t is positive we move away from the original point in the direction of v→ that right in our sketch and if t is negative we move away from the original point in the opposite direction of v→ that is left in our sketch. As t changes over all possible values we will totally cover the line. The following diagram shows this dependence on t of our sketch.
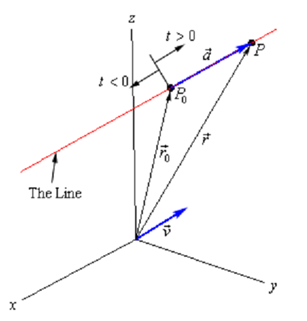
There are so many other forms of the equation of a line. To obtain the first alternate form let's start with the vector form and do a slight rewrite.
r→ = (x0 , y0 , z0) + t (a, b, c)
(x, y, z) = (x0 + ta, y0 + tb, z0 +tc)
The just one way for two vectors to be equal is for the components to be equal. In another words,
x= x0 + ta
y= y0 + tb
z = z0 +tc
The above set of equations is known as the parametric form of the equation of a line.
Note: also that this is really nothing more than an extension of the parametric equations we've seen earlier.
The only variation is that we are now working in three dimensions in place of two dimensions.
To obtain a point on the line all we do is pick a t and plug into either form of the line. In the vector form of the line we obtain a position vector for the point and in the parametric form we acquire the actual coordinates of the point.
There is one more type of the line that we wish to look at. If we suppose that a, b, and c are all non-zero numbers we are able to solve each of the equations in the parametric form of the line for t. After that we can set all of them equal to each other as t will be the same number in each. Doing this provides the following,
(x- x0) / a
= (y-y0)/ b
= (z - z0)/c
This is known as the symmetric equations of the line.