Use of Signer Certificates in Browsers
Digital certificates previously play a primary role in Internet-based cryptography systems. For instance, consider the case of a secure Web transaction that takes position when a user visits a Web storefront to compose a credit card purchase. When the user's browser accesses a protected page, a public key from the Web store has previously been delivered to the client browser in the form of an X.509 digital certificate. All this happens clearly to the user at the time the secure connection is set up.
The browser trusts the certificate because it is signed, and the browser trusts the signature for the reason that the signature can be confirmed. And, why can it be confirmed? Because the signer's public key is previously embedded in the browser software itself. To observe this in the exacting case of a browser, begin by clicking on the Security icon on the main toolbar, as shown in Figure.
Figure 2.2 the Security toolbar button in a typical browser
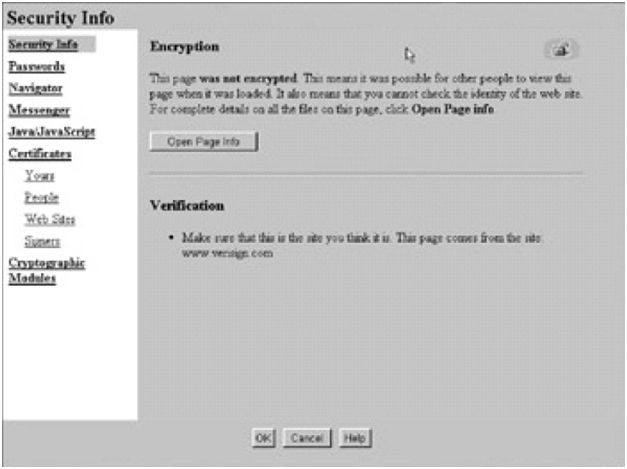
Figure: Security Info Page
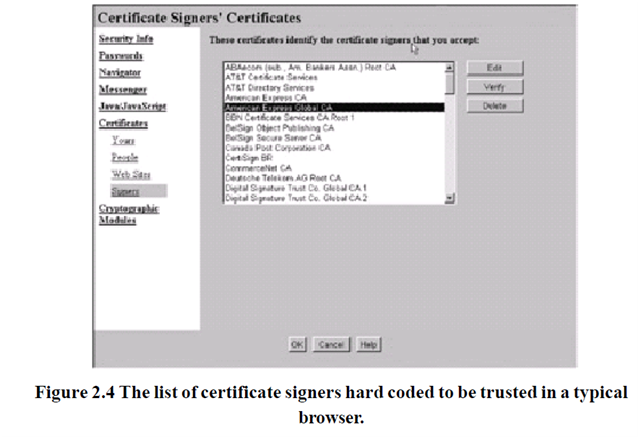
Below Certificates, select Signers, and scroll down the list, as publicized in Figure... A Window like to that shown in should show.
After that, choose a particular certificate and click on the Edit button. A demonstrate like to the one shown in Figure should come into sight.
After that, choose a particular certificate and click on the Edit button. A demonstrate like to the one shown in Figure should come into sight.
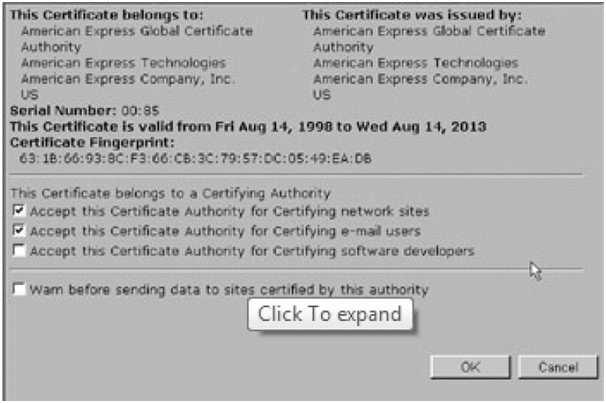
Figure 2.5 A VeriSign CA certificate embedded in a typical browser.
This is a symbol of an X.509 digital certificate. Even though X.509 certificates come in three dissimilar versions (such as the one displayed in Figure), they are the ones that are most usually encountered in today's cryptography systems. Such a certificate consists of the subsequent fields to recognize the owner of the certificate and the trusted CA that issued the certificate.
- Version
- Digital signature for the preceding fields
- Extensions
- Serial number
- Subject unique identifier
- Signature algorithm ID
- Issuer unique identifier
- Validity period
- Subject (user) name
- Issuer name
- Subject public-key information
even though only a little of the previous fields (Version, Issuer name, Validity period, Subject (user) name, Serial number, Signature algorithm ID, Subject public-key information, Issuer unique identifier, Subject unique identifier, Extensions and Digital signature for the preceding fields) that are exposed in Figure (version, serial number, issuer name, and subject name) keep in touch to the present elements in Figure, these essential elements give an plan of what such a typical certificate contains. In other words, the certificate shown in Figure 6.5 contain only a few of the basic fields. An additional detailed dump of raw certificate content might seem like the following.
Certificate: Data:
Version: v3 (0x2)
Serial Number: 8 (0x8)
Signature Algorithm: PKCS #1 MD5 with RSA Encryption
Issuer: CN=Root CA, OU=CIS, O=Structured Arts Computing Corporation, C=US Validity Not Before: Fri Dec 5 18:39:01 1997
Not After: Sat Dec 5 18:39:01 1998
Subject: CN=Test User, OU=Test Org Unit, O=Test Organization, C=US Subject Public Key Info:
Algorithm: PKCS #1 RSA Encryption
Public Key: Modulus:
00:c2:29:01:63:a1:fe:32:ae:0c:51:8d:e9:07:6b:02:fe:ec:
6d: 0e: cc: 95:4b: dc: 0a:4b:0b:31:a3:1a:e1:68:1f:d8:0b:b7:
91:fb:f7:fd:bd:32:ba:76:01:45:e1:7f:8b:66:cd:7e:79:67:
8d:48:30:2a:09:48:4c:9b:c7:98:d2:b3:1c:e9:54:2c:3c:0a:
10:b0:76:ae:06:69:58:ac:e8:d8:4f:37:83:c3:f1:34:02:6d:
9f:38:60:6f:5e:54:4f:71:c7:92:28:fb:0a:b3:44:f3:1a:a3:
fe:99:f4:3f:d3:12:e2:f8:3b:03:65:33:88:9b:67:c7:de:88:
23:90:2b
Public Exponent: 65537 (0x10001) Extensions:
Identifier: Certificate Type
Critical: no
Certified Usage:
SSL Client
Identifier: Authority Key Identifier
Critical: no Key Identifier: a7:84:21:f4:50:0e:40:0f:53:f2:c5:d0:53:d5:47:56:b7:c5:
5e:96
Signature:
Algorithm: PKCS #1 MD5 With RSA Encryption
Signature:
2d:76:3f:49:5b:53:3a:c5:02:06:a3:67:6d:d9:03:50:57:7f:de:a7:a9: cd:69:02:97:6f:66:6a:7f:95:ea:89:75:7a:fc:b0:26:81:fc:33:bb:60: e8:f7:73:77:37:f8:8a:04:3b:fc:c1:3e:42:40:3d:58:16:17:7e:47:35:
1c:73:5a: ab: 72:33:c3:f5:2b:c6: eb: b5:39:52:82:c6:3e:e1:38:c6:39:
8b: ee: e3:9f:b3:b9:29:42:0d: 11:a5:79: AF: 6d: 3a:f8:a6: ba: d0:9c:55:
48:0d: 75:91:05:0b:47:67:98:32:f3:2d:2e:49: Ed: 22: ab: 28:e8:d6:96:
a1:9b