Use of Beta to Partition Risk
The total risk or variability in earnings can be attributed to two classes of factors:
-
Marketwide factors which create variability in all securities.
-
Company specific factors which cause variability in the returns of that company's shares only.
|
The marketwide factors contribute to the systematic risk and the company-specific factors contribute to the unsystematic risk. While the systematic risk cannot be diversified away (since all shares purchased to widen the portfolio would be affected by market factors), the unsystematic risk can be diversified away.
|
The investor would like to know the exact proportions of the systematic and unsystematic risks in the total risk. To determine the systematic risk of a share, the beta (or b) of the share must be ascertained.
Systematic Risk of a Security = b2 x Variance of the Market Returns
The variance of the market returns is the variance of the returns from the market index.
Unsystematic Risk of a Security = Variance of Returns of Security - Systematic Risk
It must be noted that though the standard deviation is commonly used to denote the risk. However, while partitioning the risk, it is the variance of returns that is partitioned into systematic and unsystematic components.
The coefficient of determination may also be employed to partition the risk.
|
PERIOD
|
RETURN ON MARKET INDEX (%) (X)
|
RETURN ON SECURITY INDEX (%) (Y)
|
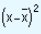
|
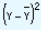 |
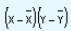 |
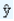 |
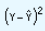 |
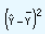 |
|
|
1
|
24
|
20
|
4
|
16
|
8.00
|
22.48
|
6.1504
|
2.5
|
|
2
|
10
|
12
|
256
|
144
|
192.00
|
11.84
|
0.0256
|
148
|
|
3
|
36
|
26
|
100
|
4
|
20.00
|
31.6
|
31.36
|
58
|
|
4
|
-16
|
-8
|
1764
|
1024
|
1344.00
|
-7.92
|
0.0064
|
1019
|
|
5
|
20
|
26
|
36
|
4
|
-12.00
|
19.44
|
43.0336
|
21
|
|
6
|
32
|
28
|
36
|
16
|
24.00
|
28.56
|
0.3136
|
21
|
|
7
|
14
|
8
|
144
|
256
|
192.00
|
14.88
|
47.3344
|
83
|
|
8
|
30
|
36
|
16
|
144
|
48.00
|
27.04
|
80.2816
|
9.20
|
|
9
|
60
|
48
|
1156
|
576
|
816.00
|
49.84
|
3.3856
|
670
|
|
10
|
50
|
44
|
576
|
400
|
480.00
|
42.24
|
3.0976
|
335
|
|
|
Total
|
260
|
240
|
4088
|
2584
|
3112.00
|
240
|
214.9888
|
2362.70
|
|
|
Mean
|
26
|
24
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Covariance
|
|
|
|
|
345.78
|
|
|
|
|
|
S.D
|
21.3125
|
16.9443
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variance
|
454.22
|
287.11
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The coefficient of determination gives us the percentage of the variation of the security's return that is explained by the characteristic line. This time the variance of the security's return gives us the systematic risk.
In our example, let us compute the systematic risk by employing both R2 and b
Total return of security = V(Y) = 287.11
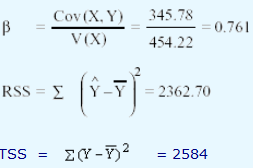
R2 = 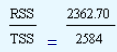 = 0.914
= 0.914
Partition of risk of security by employing β
Systematic risk=b2 x Variance of the market returns
=(0.761)2 x 454.22 = 263.05
Unsystematic risk =Variance of returns of security - Systematic risk
=287.11 - 263.05 = 24.06
Partition of risk of security by employing R2
Systematic risk =R2 x Variance of the security's return
=0.914 x 287.11
=262.42 ≈ 263.00
Unsystematic risk =Variance of returns of security - Systematic risk
=287.11 - 263.00 = 24.11