Question:
A set of processes are in a deadlock state when every process in the set is waiting for an event that can be caused by only another process in the set.
(a) There exists three different ways that an operating system can use to deal with deadlock situations. Identify the three methods, and explain how they can be used to deal with processes that are deadlocked.
(b) Assume that a system always require additional information about how resources are being requested for each process before making a decision on whether to grant the request or not to grant the request. One possible reason for not granting the request is because it can put the system in an unsafe state.
I. What is the difference between a safe state and an unsafe state in a deadlock-avoidance system?
Consider a system with 12 magnetic tape drives and 3 processes: P0, P1, P2. Process P0 requires 10 tape drives, process P1 may need as many as 4, and process P2 may need up to 9 tape drives. Suppose that at time t0, the processes are holding 5, 2 and 2 tape drives respectively, as illustrated in the table below:
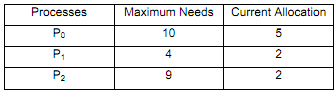
II. Is the system in a safe state at time t0? Clearly explain your answer.
III. Suppose that at time t1, process P2 requests and is allocated 1 more tape drive. Now, will this allocation put the system in a safe or unsafe state? Clearly explain your answer.