To explore the UNIX file system, use basic UNIX commands and use a text editor.
Task:
1. Logon to Linux.
2. Create a directory "Unix" under your home directory.
Command(s): .................................................
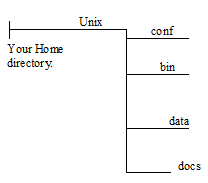
3. Create four sub-directories bin, conf, docs and data under the directory "Unix" created by you in step 2. See the directory diagram below:
Command(s): .................................................
4. Create the document called "sed-info" in your "Unix" directory using touch command.
Command: .................................................
5. Create the document called "join-info" in your "Unix" directory using touch command.
Command: .................................................
6. While in the Unix directory, move the files "sed-info" and "join-info" to directory "docs" using a single UNIX command.
Command: .................................................
7. Change to your home directory.
Command: .................................................
8. Use a single command to rename and move the "sed-info" from the "docs" directory to the "bin" directory.
Command: .................................................
9. Change to the data directory.
Command: .................................................
10. While in the data directory create a command that would copy the "sed-info" from the "bin" directory and "join-info" from the docs directory to the "conf" directory using a) absolute paths and b) relative paths.
Command (relative path): .................................................
Command (absolute path): .................................................
11. Move to your home directory. Create a single command that would delete the Unix directory and all the files and subdirectories of the Unix directory.
Command: .................................................