Types E-commerce generally based on advertising, selling, marketing and buying, but due to the differences in needs, e-commerce has been classified according to the parties of the process. It has been schemed into various schemas but the main types are: B2C, B2B, C2B and C2C. 6.1 Types of E-commerce
1 Business to Consumer, B2C:
Allow the consumer to deal directly with the business company. B2C has an advantage of eliminating the intermediation between the participants which makes the selling process much convenience. It usually gives the consumer deals with lower prices than the prices in the traditional trade. It requires typed consumer's information. In this form, both participants are almost equal in decision making.
2 Business to Business, B2B:
When trade takes place among two companies. It's complicated than B2C, because the negotiation on products, payment and shipment would take longer time than B2C according to multiple decision makers it has. This trade often generates thousands or millions of dollars. In addition, there are some strategies associated with B2B like outsourcing and off-shoring.
3 Consumer to Business, C2B:
Is a direct E-commerce between two participants, when the consumer is the vendor, the buyer is the business. Both participants are almost equal in decision making.
4 Consumer to Consumer, C2C:
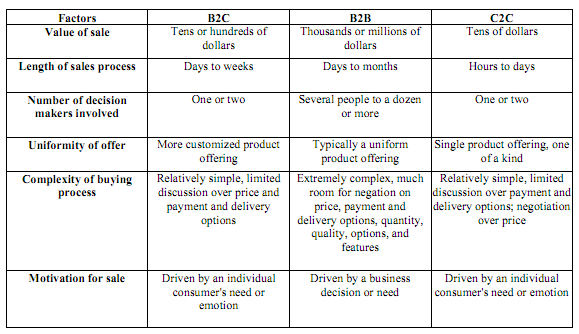
Trade takes place among two consumers. It actually works as consumers to business to consumer. Which means the transaction can't be completed without a platform -a business- to find the other participant, not a mediator. A lot of e-commerce websites are based on C2C like e-bay or Amazon, consumer 1 (vendor) will offer a product/service on the website (platform), then consumer 2 (buyer) will buy. The decision maker in this type is usually the buyer, or sometimes both of them. You can differentiate between these types in the below Table.
Table Shows the differences between B2B, B2C and C2C[1]
There are also other types for other purposes, like, e-government (We'll talk about it in the next section), e-tailing, peer to peer, business to employee, business to machine, manager to consumer, government to citizen and government to government. Applying the right type with associated strategies will increase the profitability and the productivity.
2 E-government
E-Government stands for Electronic government which also known as digital government, online government, or connected government.
It's a digital communication the uses information and communication technology to accomplish efficient communication. E-government improves the relationship between the government and its citizen by easing the information sharing, speeding the paper-based process and proving the usual formal tasks online, for instance, paying federal taxes, renewing licenses and applying for loans. E-government has many e-commerce forms such as:
1. Government-to-Citizens (G2C).
2. Citizens to Governments (C2G).
3. Government-to-Business (G2B).
4. Government-to-Government (G2G).
5. Government-to-Employees (G2E).
each with its own application.
E-government has a lot of effects and benefits in simplifying the communication between the government and other sectors like citizens, governments, businesses, and employees.
At the end, the variety of types in the market increases the demand of e-commerce and enables more efficiency and productivity if the right type applied to the suitable system. As time passes by, more types are introduced to the market to meet the needs of the current society's demands and keep people's expectations high.