Trees and Graphs
Overview: The problems for this assignment should be written up in a Mircosoft Word document. A scanned hand written file for the diagrams is also fine. Be sure to include your name and course number within all of the files that you submit.
1.Trees
Read the assigned chapter and notes for Week 5 located in the Course Documents area.
(a)
Draw a binary tree that produces the inorder traversal for the nodes in the following
order: 721, 174, 788, 828, 61, 292, 986, 3, 394, 154, 86, 229.
Hint: Y
our tree must a binary tree and not a binary search tree. The tree must produce the inorder traversal for the nodes listed in the order provided above. There are several ways that you can draw the tree for this. I recommend first drawing the nodes and links and then filling in the nodes with the correct values that produces the inorder traversal.
(b) Briefly explain some of the differences between a multiway tree and a binary search
tree.
2. Graphs
Read the assigned chapter and notes for Week 6 located in the Course Documents area.
(a) Draw the adjacency list for the following graph:
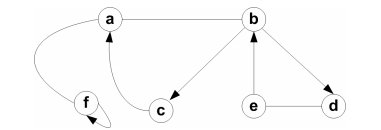
(b) Briefly state the differences between a sparse and a dense graph, and the mathematical property for each. Also, explain whether a sparse or dense graph is best implemented using and adjacency matrix and why.