Treasury securities are government bonds issued by the US Treasury Department. These are issued through the Bureau of the Public Debt. They are debt-financing instruments of the US Federal government. These securities are of four types - Treasury Bills, Treasury Bonds, Treasury Notes and Savings Bonds. All these securities, except savings bonds are highly liquid and heavily traded in the secondary stock markets.
In treasury securities, there exist on-the-run treasury securities and off-the-run treasury securities. The on-the-run treasury securities are the most recently issued US Treasury bonds and notes. Normally, stockbrokers acquire these securities in large quantities and sell them to retail investors. These securities are highly liquid and are traded at higher prices when compared to that of off-the-run treasury securities. Off-the-run treasury securities are those treasury securities, which are issued, in earlier auctions.
These securities are fixed income instruments and are free from credit risk. These securities provide low yield when compared to that of non-treasury securities. This is due to their favorable tax treatment, high liquidity, being free from credit risk, and being non-callable securities.
The relationship between the yields offered on the treasury securities for each maturity when represented graphically is refereed to as treasury yield curve. A yield curve may be an upward sloping yield curve (longer the maturity, higher the yield), inverted yield curve (longer the maturity, lower the yield), or a flat yield curve (same yield regardless of maturity).
Figure 1: US Treasury Yield Curve
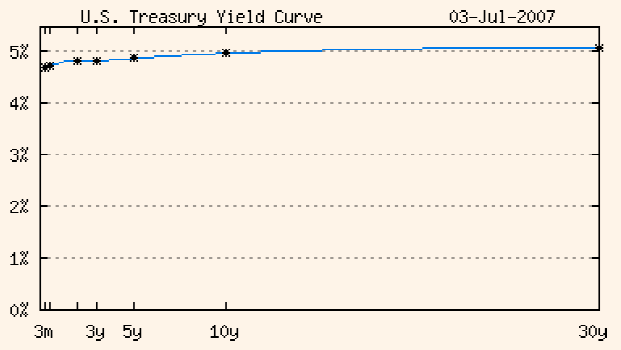
Table 1
|
Maturity
|
Yield on 03.07.2007
|
Yield on 02.07.2007
|
|
3 Month
|
4.71
|
4.65
|
|
6 Month
|
4.74
|
4.71
|
|
2 Year
|
4.83
|
4.85
|
|
3 Year
|
4.83
|
4.87
|
|
5 Year
|
4.87
|
4.91
|
|
10 Year
|
4.97
|
5.01
|
|
30 Year
|
5.07
|
5.10
|
From the above two exhibits, it is clear that the longer the maturity, the higher will be the yield. Due to this feature, treasury yield curve is also known as the 'upward sloping yield curve' or the 'normal yield curve'.