The five d orbitals with distinct values of the magnetic quantum number (m) have the similar energy in a free atom or ion. In any compound they interact differently with the surrounding ligands and a ligand field splitting is performed. The common coordination is octahedral (Oh point group) with six surrounding ligands. Then two of the d orbitals are required at higher energy than the other three (dxz, dxy and dyz, known as t2g). Such a splitting happens in any transition metal compound with octahedral coordination, including aqua ions and several solids. Electronic transitions between eg and t2g orbitals show rise to colors, which are a similar feature of transition metal complexes, and allow Δo to be measured experimentally.
Although originally explained in terms of electrostatic repulsion between the ligands d and electrons, it is now defined that ligand field splittings come from the similar type of orbital overlap effects as donor-acceptor interactions.
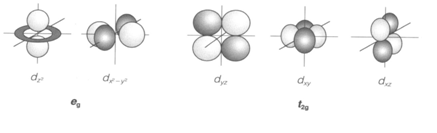
Fig. The five d orbitals, showing eg and t2g sets in an octahedral complex, with ligands along the x, y and z axes.
Most ligands coordinate to the metal ion giving nonbonding electrons. A ligand lone-pair orbital pointing directly to the metal comes with the eg orbitals (1) but has the wrong symmetry to communicate with t2g. The overlap shows rise to antibonding and σ bonding molecular orbitals . The bonding orbitals are covered by the electrons from the ligand, and it is the σ antibonding levels that form the 'metal' eg set, require for the d electrons of the metal ion. A rigid σ-donor ligand can give a large splitting Δo by raising the eg energy, π bonding arises when ligands have orbitals directed perpendicular to the metal-ligand axis, which may communicate with the metal t2g orbitals (2)
The order of Δo values gives by different ligands is known as the spectrochemical series. A partial series in order of increasing splitting is:
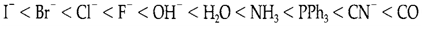
As expected, rigid donors are usually high in the series, π donors are low, and π-acceptor ligands such as CO and CN- are among the highest, and known as strong field ligands. The major trends with different metal ions are (i) Δo increases with charge on the ion, and (ii) splittings are bigger for 5d and 4d series elements than in the 3d series.