Transition Curves:
If a vehicle travelling on a straight enters a horizontal curve abruptly, it will cause shock and sway. To avoid this, it is customary to provide a transition curve (Figure). Incidentally, the transition curve is also used to provide gradual application of super- elevation and widening of the curve. A spiral is the most commonly used transition curve.
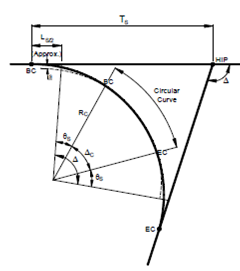
Figure: Main Elements of a Circular Curve Provided with Transitions
Some of the important properties of the spirals are given below :
(a) Ls Rc = LR = constant
(b) L = M√ θ , where M is a constant
M = √2RL
Also, L = 2 Rθ
(c) θ= (L/Ls)2 θs
(d) θs = Ls/2Rc radians = 28.65 Ls/Rs degrees
(e) Ts = Ls/2 +(Rc+s)tan(Δ/2)
(f) s= Ls2/24Rc
(g) Es= (Rc+s)sec Δ/2-Rc
The following nomenclature may be noted:
θs : Spiral angle
Δc : Angle of the circular curve
Δ : External angle
Ls : Spiral Length
Rc : Radius of circular curve
L : Length of spiral from starting point to any point
R : Radius of curvature of the spiral at the point distant L from starting point
θ : Deflection angle at any point of the spiral distant L from the starting point
Ts : Tangent distance
Es : Apex distance
s : Shift
HIP : Horizontal Intersection Point
BS : Beginning of spiral
BC : Beginning of circular curve
EC : End of circular curve
ES : End of spiral