The Linux Process Scheduler uses time slice to prevent a single process from using the CPU for too long. A time slice specifies how long the process can use the CPU. In our simulation, the minimum time slice possible is 10ms and the maximum time slice possible is 300 ms. The scheduler assigns higher time slices to processes that are more interactive and lower time slices to processes that are more CPU intensive. Note that time slice is a positive integer in this range [10, 300]. To calculate the time slice, we use this formula:
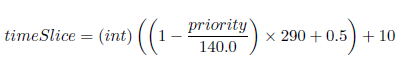
Each process is supplied with a priority level that ranks a process based on their worth and need for processor time. The priority levels range from 100 to 140 [100,140]. Processes with a lower priority will run before a process with a higher priority. Process with a lower priority level also receives a longer time slice. A process's initial priority (sometimes called static priority) is calculated based on its nice value. Nice values range from -20 to +19 [-20, 19] indicating how nice the process is. Larger nice values correspond to a lower priority. CPU intensive processes typically have higher nice values while IO bound processes have lower nice values. Nice values are provided with the input file. Note that a priority value is a positive integer in this range
[100,140]. To calculate the initial (or static) priority we use this formula:
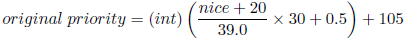
After a process exhausts its time slice, it will join the expired queue or go back to the active queue. Before doing that, it has to calculate its new priority (sometimes called the dynamic priority). This is the formula used to calculate the dynamic priority:
priority = original priority + bonus:
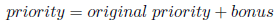
Bonus points are given to processes that either use too much or too little CPU time. Bonus points are integers range from -5 to +5 ([-5, 5]). Here are the guidelines to calculating bonus points:
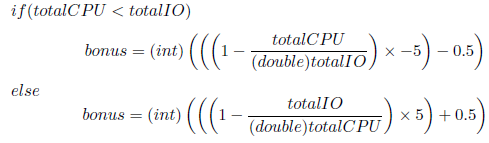
Note : Here total IO mean the total time spent in the IO queue to this point and total CPU mean the total time spent in the CPU to this point.