Thrust reversal:
Thrust reversal is a means of reducing the landing run of an aircraft without excessive use of wheel brakes or the use of braking parachutes. On a propeller driven aircraft (piston and turbo prop), reverse thrust can be obtained by reversing the pitch of the propellers. On a pure turbo-jet this is not possible and the only simple and effective way of slowing the aircraft down quickly is to reverse the power as a deceleration force. This method is much safer than wheel brakes when landing on ice or snow covered runways.
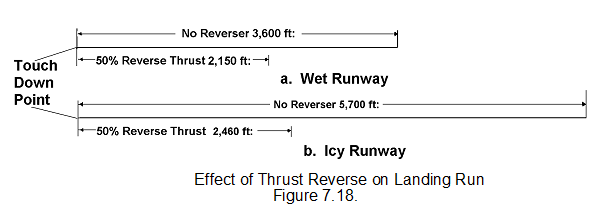
It can on some aircraft also be used to reduce speed in flight thus allowing a rapid rate of descent without an air brake system. The difference in landing distances between the same aircraft without reverse thrust and using reverse, is shown.
To obtain reverse thrust, the jet efflux must be given a forward component of velocity. The mechanism to achieve this should fulfil the following requirements:
a. A reasonable amount of thrust (50% of take-off thrust would be adequate) should be available in the reverse direction.
b. The reverser should not affect the normal working of the engine and there should be no appreciable loss of thrust or increase in specific fuel consumption (SFC).
c. When in use, the reverser should not cause debris or excessive amounts of hot air to enter the intake.
d. The discharged hot gases should not impinge on parts of the aircraft (eg. nacelles, tyres, landing flaps, cabin windows, etc.). Impingement of the turbulent gas stream may cause damage by vibration as well as by heating.
e. Fire hazards must be avoided. Hydraulic and lubricating systems should not be fitted near the jet pipe.
f. Weight, complexity and cost must be kept to a minimum.
g. The reverser must not operate until required to do so. It is necessary to ensure that:
1. Accidental selection of reverse thrust is impossible.
2. No single failure in the operating system selects reverse thrust.
3. The thrust changing elements are biased away from the reverse thrust position.