Thrust diagrams for the beam:
Illustrate the shear force, bending moment & thrust diagrams for the beam illustrated in Figure
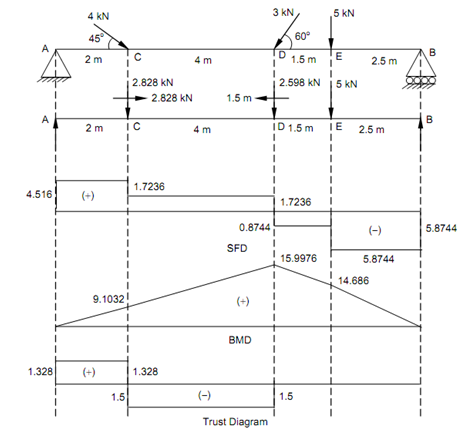
Figure
Solution
Vertical component of 4 kN at C, = 4 × sin 45o = 2.828 kN ( ↓ )
Horizontal component of 4 kN at C, = 4 × cos 45o = 2.828 kN ( → )
Vertical component of 3 kN at D, = 3 × sin 60o = 2.598 kN ( ↓ )
Horizontal component of 3 kN at D, = 3 × cos 60o = 1.5 kN ( ← )
Taking moments around B,
RB × 10 - 5 × 7.5 - 2.598 × 6 - 2.828 × 2 = 0
RB = 5.8744 kN
RA = 2.828 + 2.598 + 5 - RB = 10.426 - 5.8744
RA = 4.5516 kN
Shear Force (Beginning from the Left End A)
SF at A, FA =+ 4.5516 kN
SF just left of C, FC =+ 4.5516 kN
SF just right of C, FC =+ 4.5516 - 2.828 =+ 1.7236 kN
SF just left of D, FD =+ 1.7236 kN
SF just right of D, FD = + 1.7236 - 2.598 = - 0.7844 kN
SF just left of E, FE =- 0.8744 kN
SF just right of E, FE =- 0.8744 - 5 =- 5.8447 kN = Reaction at B.
Bending Moment (Beginning from the Right End B)
BM at A and B, MA = MB = 0
BM at E, M E = + (5.8744 × 2.5) = + 14.686 kN-m
BM at D, M D = + 5.8744 × 4 - 5 × 1.5 = + 15.9976 kN-m
BM at C, M C = + (4.5516 × 2) = + 9.1032 kN-m (considering left side)
Maximum Bending Moment
It shall occur at D where SF changes sign.
Thus, M max = + 15.9976 kN-m
Thrust Diagram
Let us find out the horizontal reaction at A (being a hinged end).
∑ H = 0
+ H A - 2.828 + 1.5 = 0
∴ H A = 1.328 kN
The section AC is subjected to 1.328 kN (tensile force).
The section CD is subjected to 1.5 kN (compressive force).
∴ (2.828 - 1.328 = 1.5)