In algebra knowing that 23 = 8 is not sufficient. Equally important to know is what would be the result if quantities like 23 . 2-4 . 26 or 37 / 32 are simplified. Mind you, finding the value of quantities like these in most of the problems is not an end in itself. The values of these quantities form an input for solving the problem further. Hence, simplifying these quantities help us to solve more advanced problems. Also that, one feels monotonous if he tries to simplify quantities like these by stating at each step what they literally mean. In this part we learn about the laws of indices and understand the logic behind these concepts.
Law 1
am x an = am+n, when m and n are positive integers.
By the above definition, am = a x a ...... to m factors and
an = a x a .... to n factors.
am x an = (a x a...to m factors) (a x a...to n factors)
= a x a .................... to m + n factors
= am+n
Now we extend this logic to negative integers and fractions. First let us consider this for negative integer, that is, m will be replaced by - n. By the definition of
am x an = am+n, we get
a-n x an = a-n+n = a0
But we know that a0 = 1
| Hence, a-n |
= |
1/ an |
or an |
= |
1/ a-n . |
Similarly, what would be the case if m = p/q and n = p/q. By definition, we have
ap/q x ap/q = ap/q + p/q = a2p/q
This can be written as 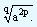 This is similar to taking the qth root of a2p. Now what would be the result if we proceed to multiply ap/q, q number of times. That is,
This is similar to taking the qth root of a2p. Now what would be the result if we proceed to multiply ap/q, q number of times. That is,
ap/q x ap/q x ap/q x ap/q ........... to q factors will be equal to aqp/q
We express this as (ap/q)q= ap, that is taking the qth root of ap.
Apart from these we look at the meaning of a0. In this case the value of m = 0. Therefore, by definition
a0 x an = a0+n = an
| This can be also expressed as a0 |
= |
an /an |
= |
1. |
Now we take a numerical and check the validity of this law.
26 x 27 = (2 x 2 .... to 6 factors)
(2 x 2 ...... to 7 factors)
or, 26+7 = 2 x 2 ....... to (6 + 7) factors
= 213 = 8192
or else,
26 x 27 = (2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2) x
(2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2)
= (64)(128)
= 8192
(Note: The same logic can be extended to more than two factors also.)
Law 2
am/an = am-n, when m and n are positive integers and m > n.
By definition, am = a x a ....... to m factors and
an = a x a ....... to n factors
| Therefore, am |
/ |
an |
= |
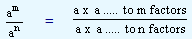 |
|
|
| |
|
|
= |
a x a ....... to m - n factors |
| |
|
|
= |
am-n |
Now we take a numerical and check the validity of this law.
|
27
|
/
|
24 |
= |
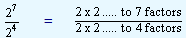 |
|
|
| |
|
|
= |
2 x 2 x 2......to (7 - 4) factors |
| |
|
|
= |
2 x 2 x 2......to 3 factors |
| |
|
|
= |
23 = 8 |
or else,
| 27 |
/ |
24 |
= |
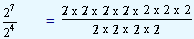 |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
= |
2 x 2 x 2 = 21+1+1 = 23 |
| |
|
|
|
|
= |
8 |
Law 3
(am)n = amn, when m and n are positive integers.
| By definition, (am)n |
= |
am x am x am .... to n factors. |
| |
|
(a x a ... to m factors) ....... to n times |
| |
= |
a x a ..... to mn factors |
| |
= |
amn |
Now let us look whether this is true for positive fractions. We will keep m as it is and replace n by p/q, where p and q are positive integers. Then we will have
(am)n = (am)p/q
Now the qth power of (am)p/q = {(am)p/q}q
| = |
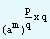 |
| = |
(am)p |
| = |
amp |
If we take the qth root of the above, we obtain
| (am)p/q |
= |
 |
For n being any negative quantity: In this case also m remains the same and n be replaced by - r, where r is positive. Then we have
|
(am)n
|
= |
(am)-r |
= |
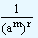 |
|
=
|
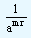 |
= |
a-mr |
Again replacing -r by n, we obtain amn.
Now with the help of a numerical example let us verify this law.
| (24)3 |
= |
24 x 24 x 24 |
| |
= |
24+4+4 |
| |
= |
212 = 4096 |
| or else, |
|
|
| (24)3 |
= |
(24) (24) (24 ) |
| |
= |
(2 x 2 x 2 x 2) (2 x 2 x 2 x 2) |
| |
|
(2 x 2 x 2 x 2) |
| |
= |
(16) (16) (16) |
| |
= |
4096 |