The retina – the light detector of the eye:
The physical aspects of the retina:
1.The absorption of a light photons in a photoreceptor triggers an electrical signal to the brain-an action potential fig(4).
2. The energy of the photon is about 3 eV: the action potential has an energy millions of times greater.
3. The light photons apparently causes a photo chemical reaction in the photoreceptor which in some way initiates the action potential.
4.the photon must be above the minimum energy to cause the reaction.
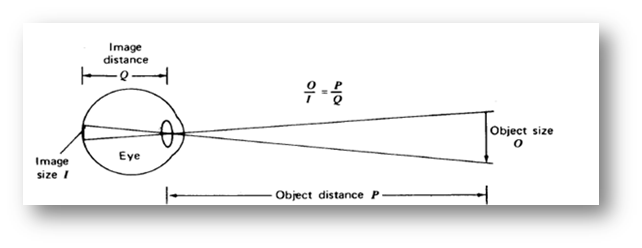
The image on the retina is very small .A convenient equation for determining the size of the image on the retina comes from the ratios of the lengths of the sides of similar triangle fig (4).
O/P=I/Q
Where O is the object size ,I the image size ,P the object distant and Q the image distance usually about 2 cm. Fig(5)
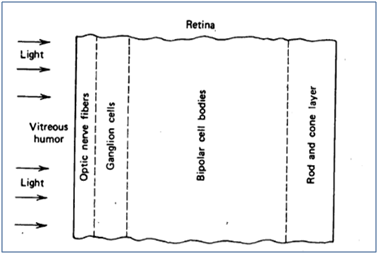
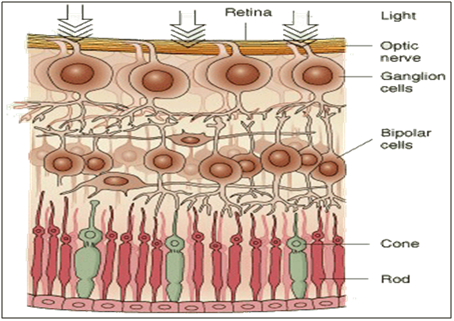
There are two photoreceptor in the retina:
The cones and the rods .Though out most of the retina cones and rods are not on the surface of the retina but lie behind several layers of nerve tissue through which the light must pass fig(6) The rods and cones distributed symmetrically in all directions from the visual axis except in one region- the blind spot.
-The rods are used for night or scayopic vision and for peripheral vision, they are much more abundant than the cones(~120 million in each eye).
- The rods are most sensitive to blue- green light(~510 nm).
The blind spot: It is a region from about 13o to 18o that has neither cones nor rods ,this is the point at which the optic nerve.
-The cones (~ 6.5 million in each eye),they are primarily used in day light or photopic vision.
- With cones we can see fine details and recognize deferent colors.
- The cones are not uniformly sensitive to all colors but have maximum sensitivity at about 550 nm in the yellow- green region .