Primary Model
Below is a regression analysis without 17 outliers that have been removed
Regression Analysis: wfood versus totexp, income, age, nk
The regression equation is
wfood = 0.378 - 0.00129 totexp - 0.000054 income + 0.00170 age + 0.0317 nk
Predictor Coef SE Coef T P VIF
Constant 0.37816 0.01356 27.89 0.000
totexp -0.00128554 0.00006284 -20.46 0.000 1.324
income -0.00005410 0.00004950 -1.09 0.275 1.341
age 0.0016993 0.0003058 5.56 0.000 1.065
nk 0.031717 0.004676 6.78 0.000 1.007
S = 0.0880161 R-Sq = 28.0% R-Sq(adj) = 27.8%
Analysis of Variance
Source DF SS MS F P
Regression 4 4.5159 1.1290 145.73 0.000
Residual Error 1497 11.5970 0.0077
Lack of Fit 1328 10.1731 0.0077 0.91 0.806
Pure Error 169 1.4239 0.0084
Total 1501 16.1129
Secondary Model
Below is a regression analysis without 17 outliers that have been removed and dropping the income variable
Regression Analysis: wfood versus totexp, age, nk
The regression equation is
wfood = 0.376 - 0.00132 totexp + 0.00165 age + 0.0317 nk
Predictor Coef SE Coef T P VIF
Constant 0.37593 0.01341 28.04 0.000
totexp -0.00131710 0.00005581 -23.60 0.000 1.045
age 0.0016462 0.0003019 5.45 0.000 1.038
nk 0.031672 0.004676 6.77 0.000 1.007
S = 0.0880218 R-Sq = 28.0% R-Sq(adj) = 27.8%
Analysis of Variance
Source DF SS MS F P
Regression 3 4.5067 1.5022 193.89 0.000
Residual Error 1498 11.6063 0.0077
Lack of Fit 644 4.9570 0.0077 0.99 0.560
Pure Error 854 6.6493 0.0078
Total 1501 16.1129
The Null Hypothesis - H0: No difference between the primary and secondary model
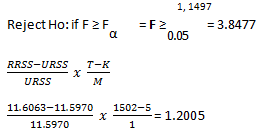
Since the F value is 1.2005 < 3.8477 there is sufficient evidence to suggest that we accept H0 implying that there is no difference between the primary and secondary model and income can be removed.