The Concept of Process
Informally, a method is a program in execution, behind the program has been loaded in the main memory. However, a method is more than just a program code. A process has its own value of program counter, address space, threads, and temporary variables, file handles, security attributes, return addresses etc.
Each process has a life cycle, which consists of execution, creation and termination phases. A process may create numerous new processes, which in turn may also make a latest process. In UNIX operating system surroundings, a new process is shaped by fork system call. Process creation needs the subsequent four actions:
i) Setting up the process description: Setting up the process description need the design of a Process Control Block (PCB). A PCB includes basic data such as, process status, owner, description of the allocated address space, process identification number, and much other implementation dependent process explicit information essential for process management.
ii) Allocating an address space: There are only two ways to allocate address space to processes: allocating separate space to each process or sharing the address space among the created processes
iii) Loading the program into the allocated address space: The executable program file is fully loaded into the allocated memory space.
iv) Passing the process description to the process scheduler: Once, the three steps ofProcess formation as mention above are finished, the information gathered through the above-mentioned steps is sent to the process scheduler who allocate processor(s) resources to many competing to-be-executed processes queue.
The process execution phase is guarded by the process scheduler. Process scheduling may be per thread or per process. The process scheduling engage three concepts: state transition, process state, and scheduling policy.
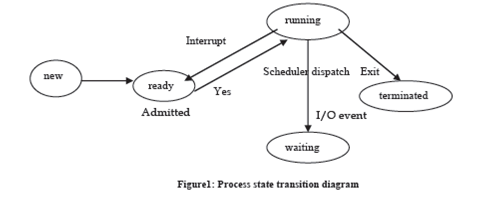
A process may be in one of the following states:
(1) Running: The process is being implemented on a multiple processors or Single processor.
(2) New: The process is being formed.
(3) Ready: The process is prepared to be executed if a processor is accessible.
(4) Waiting: The process is coming up for some event to happen.
(5) Terminated: The process has complete execution.
At the time, a process may be in some one of the above mentioned states. As soon as the process is declare into job queue, it goes into equipped state. When the process scheduler transmits the process, its state become running. If the process is completely executed then it is terminated and we say that it is in final state. However, the process may go back to complete state due to some interrupts or may go to ahead of you state due to some I/O activity. When I/O activity is ended it may go to ready state. The state transition diagram is shown in Figure 1:
The scheduling policy may be also pre-emptive or non pre-emptive. In pre-emptive policy, the process can be interrupted. Operating systems have dissimilar scheduling policies. For example, to select a process to be implemented, one of the best scheduling policy may be: First In First Out (FIFO).When the process completed execution it is ended by system calls like abort, releasing all the allocated resources.