The Budget Line: The Consumer Constraints
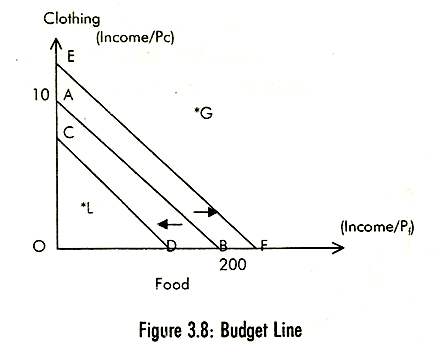
The consumer would like to maximize his satisfaction by reaching the highest possible indifference curve. But in the process, he faces constraints in form of his income and prices of goods and services for which he has to make payment. The budget line shows various combinations of food and clothing that a consumer can purchase given his money income and prices of the two goods. Suppose the consumers' money income (M) is Rs 600 per week and the price of food (Pf) is Rs 3 and the price of clothing (Pc) is Rs 60. Fig. 3.8 shows that if the consumer spends all his income on food, he would buy 200 units of food per week (point B). On the other hand, if he spends all his income on clothing he could buy 10 units of clothing per week (point A).
By joining points A and B by a straight line we define budget line AB. Thus, the budget line depicts 'all combinations of two goods that a consumer can purchase by spending his given money income on the two goods at their given prices. Each such combination is represented by a point on the budget or price line.
The budget equation can be written in the form:
QX, Pf + Qy.Pc = M
where Qx and Qy are the respective quantities of food and clothing purchased.
Slope of AB = Pf /Pe
Any point outside the given price line, like G, is not attainable by the consumer and at point L the consumer underspends his income. An increase in the money income, prices remaining constant or an equal proportionate increase in prices (ceteris paribus), shifts the budget line upwards parallel '(line EF) to the original budget line. Similarly, a decrease in the money income shifts the budget line downwards (line CD).
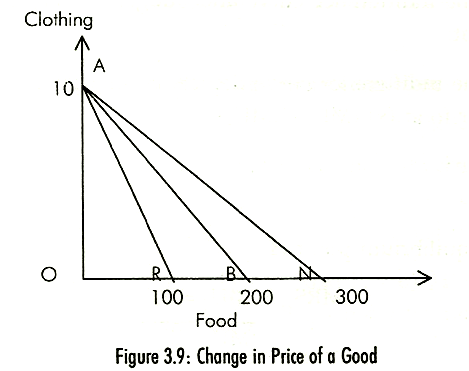
With a change in price, the budget line will rotate on the axis representing the good whose price has changed, money income and price of the other good remaining constant. A decrease in the price of the good pivots the budget line to the right or outwards and vice versa. In Fig. 3.9 a decrease in the price of food to Rs 2 rotates the budget line to the position AN and an increase in price to Rs 6 pivots the budget line inwards to AR.