The Null Hypothesis - H0: There is no heteroscedasticity i.e. β1 = 0
The Alternative Hypothesis - H1: There is heteroscedasticity i.e. β1 0
Reject H0 if Q = ESS/2 > 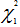
MTB > let k2=sum(c20)/1519
MTB > let c22 = c20/k2
C20 = sqres
C22 = gt
Regression Analysis: gt versus income, totexp, age, nk
The regression equation is
gt = 1.15 + 0.000130 income - 0.00135 totexp + 0.00095 age - 0.0424 nk
Predictor Coef SE Coef T P
Constant 1.1494 0.2336 4.92 0.000
income 0.0001296 0.0007340 0.18 0.860
totexp -0.001345 0.001034 -1.30 0.193
age 0.000948 0.005248 0.18 0.857
nk -0.04239 0.08131 -0.52 0.602
S = 1.54236 R-Sq = 0.1% R-Sq(adj) = 0.0%
Analysis of Variance
Source DF SS MS F P
Regression 4 5.364 1.341 0.56 0.689
Residual Error 1514 3601.594 2.379
Total 1518 3606.958
Source DF Seq SS
income 1 0.443
totexp 1 4.195
age 1 0.080
nk 1 0.647
MTB > let k3 = 5.364/2
MTB > print k3
Data Display
K3 2.68200
Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function
Chi-Square with 2 DF
P( X <= x ) x
0.95 5.99146
MTB > # since Q=ESS/2 = 2.68200 < chi = 5.99 we have no hetero from Breusch-Pagan Test
Since Q = 2.68200 < 5.99 = 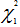 , there is sufficient evidence to accept H0 which suggests that there is no heteroscedasticity from the Breusch-Pagan test at 5% significance level which means that one or more slopes are zero.
, there is sufficient evidence to accept H0 which suggests that there is no heteroscedasticity from the Breusch-Pagan test at 5% significance level which means that one or more slopes are zero.