Surface Drainage:
Surface drainage deals with arrangement for quickly leading the water from rainfall away from the surface of pavements, shoulders, slopes of embankments and cuts. The rain water falling on the pavement and shoulders is lead away by providing a suitable camber on a single carriageway road or cross-fall on a dual carriageway road (Figure).
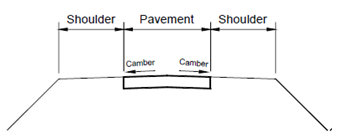
Figure (a) : Camber on single Carriageway Road
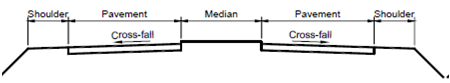
Figure (b): Cross-fall on Dual Carriageway Road
The values of camber/cross-fall normally followed in India are given in Table 1.
Table : Values of Camber
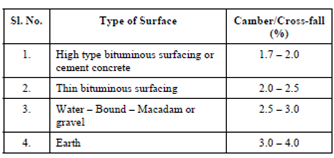
The shoulder is provided with a slope 0.5-1.0 percent steeper than the camber/cross-fall of the pavement.
The run-off is dependent on the intensity of rainfall. The formula used is:
Q = 0.028 PIc A
where Q = Run-off in cu m per sec,
P = Coefficient of run-off depending upon the nature of surface having values ranging from 0.40 for permeable surfaces to 0.90 for concrete or dense bituminous surfaces,
Ic = Critical intensity of storm in cm per hour, and
A = Catchment area in hectares.