Substitution Rule
∫ f ( g ( x )) g′ ( x ) dx = ∫ f (u ) du, where, u = g ( x )
we can't do the following integrals through general rule.
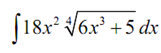
This looks considerably more difficult. Though, they aren't too bad once you illustrated how to do them. Let's begin
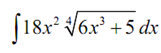
In this let's notice that if we let
u = 6 x3 + 5
and we determine the differential for this we get,
du = 18x2 dx
Now, let's go back to our integral & notice as well that we can remove every x which exists in the integral and write down the integral totally in terms of u by using both the definition of u & its differential.
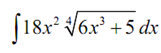 = ∫ (6 x3 + 5)4 (18x2 dx )
= ∫ (6 x3 + 5)4 (18x2 dx )
= ∫ u (1/4) du
In the procedure of doing this we've taken an integral which looked very hard and with a rapid substitution we were capable to rewrite the integral in a very easy integral which we can do.
Evaluating the integral gives,
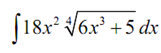 = ∫u (1/4) du=(4/5)u(5/4) + c = (4/5)(6x3+5)(5/4)+c
= ∫u (1/4) du=(4/5)u(5/4) + c = (4/5)(6x3+5)(5/4)+c
As always we can verify our answer with a rapid derivative if we'd like to & don't forget to
"back substitute" & get the integral back into terms of the original variable.
What we've done above is called the Substitution Rule. Following is the substitution rule in general.
A natural question is how to recognize the correct substitution. Unluckily, the answer is it totally depends on the integral. Though, there is a general rule of thumb which will work for several of the integrals that we're going to be running across.
While faced with an integral we'll ask ourselves what we know how to integrate. Along the integral above we can quickly recognize that we know how to integrate
∫ 4 x dx
As a final note we have to point out that frequently (in fact in almost every case) the differential will not seems exactly in the integrand as it did in the example above & sometimes we'll have to do some manipulation of the integrand and/or the differential to obtain all the x's to disappear in the substitution.