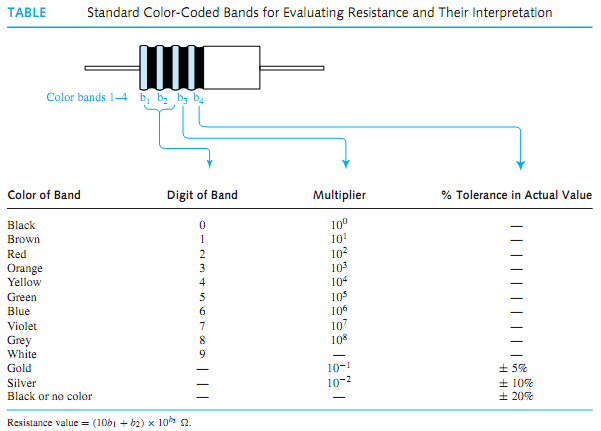
Standard Color-Coded Bands for Evaluating Resistance
Practical resistors are manufactured in standard values, various resistance tolerances, several power ratings (as will be explained shortly), and in a number of different forms of construction. The three basic construction techniques are composition type, which uses carbon or graphite and is molded into a cylindrical shape, wire-wound type, in which a length of enamel-coated wire is wrapped around an insulating cylinder, and metal-film type, in which a thin layer of metal is vacuum deposited. Table illustrates the standard color-coded bands used for evaluating resistance and their interpretation for the common carbon composition type. Sometimes a fifth band is also present to indicate reliability. Black is the least reliable color and orange is 1000 times more reliable than black.
For resistors ranging from 1 to 9.1 �, the standard resistance values are listed in Table. Other available values can be obtained by multiplying the values shown in Table by factors
of 10 ranging from 10 � to about 22 × 106 �. For example, 8.2 Ω �,82Ω �, 820Ω �, . . . , 820Ω k� are standard available values.
The maximum allowable power dissipation or power rating is typically specified for commercial resistors. A common power rating for resistors used in electronic circuits is 1�/4 W; other ratings such as 1�/8, 1/�2, 1, and 2 W are available with composition-type resistors, whereas larger ratings are also available with other types. Variable resistors, known as potentiometers, with a movable contact are commonly found in rotary or linear form. Wire-wound potentiometers may have higher power ratings up to 1000 W.