Sphere packing
Element structures where chemical bonding is nondirectional are best explained by considering the packing of equal spheres. Close-packed structures are ones that full space most efficiently. In two dimensions this is acquired in a layer with each sphere surrounded hexagonally by six others. Three-dimensional structures are designed by stacking these layers so that the spheres in one layer fall over the hollows in the one below. Having placed two layers, labeled B and A, there are alternative positions for the spheres in the third layer. They could be placed directly over spheres in the first layer A to give a linear sequence denoted ABA. Alternatively, the spheres in the third layer can be placed in positions where there are gaps in layer A; two such spheres labeled C are shown A regular packing based on this latter arrangement should then place the fourth layer directly over layer A, giving a linear sequence denoted ABCA. The simplest three-dimensional close-packed structures are based on these two regular sequences of layer ranks:
ABABABAB...gives hexagonal close packing (hcp);
ABCABCABC...gives cubic close packing (ccp).
These structures are explained respectively. In the ccp arrangement, successive close-packed layers are ranked along the body diagonal of a cube. The unit cell shown is based on a cube with atoms in the face positions, and the structure is also known as face-centered cubic (fcc).
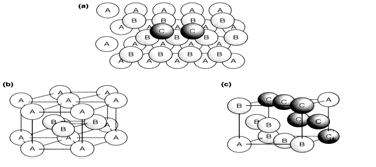
Fig. 1. Close-packed structures, (a) Stacking of layers showing the sequence ABC (see text); (b) the hcp structure; (c) one unit cell of the fcc structure.
In both hcp and fcc structures each sphere is surrounded by 12 others at the same near-neighbor distance. (There are six similar close-packed layer, and three each in the layers above and below.) If the spheres are in contact both structures give 74% filling of space by the spheres, with the remaining 26% outside them. That is the optimum space filling possible with equal spheres. Same types of close-packed structures can be constructed from more complicated sequences of layers such as ABABCABABC..., or even with random sequences. Although these are sometimes achieved, most close-packed structures are of the simple hcp or fcc types.