Space Allocation Utilization and Management of library building in library managenent
Library planning constitutes correct estimation of space required for various activities, logical juxtaposition of space earmarked for various activities and optimal use of the space available. Since it is within the confines of a library building that most library activities take place (some of the activities may be profitably carried out outside the confines of the library e.g, binding in many libraries is done by outside professional binders; computer operation may be carried out in the central computer facility of the institution or subcontracted to some outside agencies), rational estimation of space requirement and optimal utilisation of space is 'sine qua non' of successful library management. For operation, the library needs space for books (all types of documents), users and staff. Books are to be stored and, displayed in specific areas and in special furniture, equipment has to be housed in special rooms, readers are to be provided with tables and chairs located in congenial reading rooms or study carrels. The staff needs space to work undisturbed (and without disturbing others-the effect of a typist sitting in a reading room is easily imaginable!). Provision of these space requirements is vital in the planning of a library building.
Mainly the following four broad areas along with their allied and sub-areas are identified as common service areas in a library:
a) Circulation area, which includes:
- Stack rooms or halls
- Charging Desk
- Public Catalogue/s
b) Reader Activity Area, which includes:
- Reading room/s
- Microform reading room
- Study carrels
c) Staff Activity Area, which includes:
- Acquisition section
- Technical section
- Reference section
d) Other Areas, which include:
- Senior professionals rooms
- Space for library staff
- Seminar room
- Binding section
- Reprography section
(see Appendex 2 for a case study of estimation of space requirement for a-special library.)
Some important tips for space management 'in library building are given below.
- Flexibility is the catchword
- Function is more important than beauty
- Evolutionary steps in orientation & shape of building are I, T, L, U & O
- Shape: a 3:2 rectangle with door half way along long wall of not more than 100 ft. long and not more than 4 floors is ideal for best ratio of assignable to gross area, most direct traffic and transportation and ease in organising, integrity and adding or enlarging.
- Primary floor and entrance should be on grade
- Primary floor should be larger than other floors
- Building parameter should be as straight and uncluttered as possible
- Security and fire safety should be incorporated on priority
- Minimise RCC
- Avoid space stealors like' balconies, air wells, light wells, etc
- Minimise interior walls
- Don't overuse glass
- All assignable space should take a floor load of 150 lb/sq.ft (250-300 lb/sq.ft. for compact storage)
- Simple open forms should be prefered
- Informal comfortable atmosphere need to be created
- Accessibility and convenience are very important
- Noise control should be looked into
- Space allocation is an important activity which need to be done logically and scientifically. It is better to consider floor as a series of concentric circles with the centre being the place where elevator, main stair case and entrance are located. Even considering space three-dimensionally, the same principle holds. Then proceed with radial assignment of space to various activities.
- The relationship between units has to be decided in a heuristic method by drawing charts with different intensity of relationships between units like essesntial, important, desirable, not important and undesirable.
- Seating economies like size of tables, and stealing space from aisles to be given due consideration.
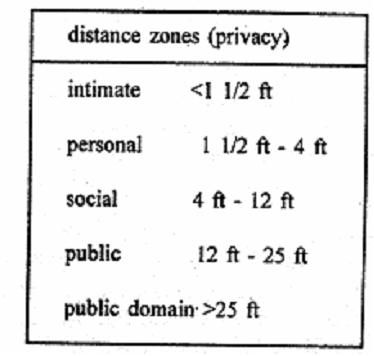
It is here that the finding of the past studies both in librarianship as well as other areas like behavioural science and psychology have to be - noted. For example, it has always been reported that users prefer to occupy empty tables even if it is little away in the reading hall. The next preferred seat in a four seater table is diagonal position and the last chance is sitting by the side of another user. Similarly the distance zones of privacy reported by psychologists given below should help us to determine the seating arrangements in different areas.