Solve the subsequent quadratic equation:
Solve the subsequent quadratic equation through taking the square roots of both sides.
3x2 = 100 - x2
Solution:
Step 1. Using the addition axiom, add x2 to both sides of the equation.
3x2 + x2 = 100 - x2 + x2
4x2 = 100
Step 2. Using the division axiom, divide both sides of the equation through 4.
4x 2 /4 = 100/4
x2 = 25
Step 3. Take the square root of both sides of the equation.
x2 = 25
√x2 = √25
x = ±5
Thus, the roots are x = +5 and x = -5.
Step 4. Check the roots.
3x2 = 100 - x2
3(±5)2 = 100 - (±5)2
3(25) = 100 - 25
75 = 75
If a pure quadratic equation is written in common form, a general expression can be written for its roots. The common form of a pure quadratic is the subsequent.
ax2 + c = 0
Using the subtraction axiom and subtract c from both sides of the equation.
ax2 = -c
Using the division axiom and divide both sides of the equation by a.
x2 = - c/a
Now take the square roots of both sides of the equation.
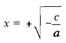
Therefore, the roots of a pure quadratic equation written in common form ax2 + c = 0 are 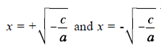 .
.