SIMPLE EPITHELIA (UNILAYERED EPITHELIA) -
1. SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM (PAVEMENT EPITHELIUM) -
- It is composed of large flat cells whose edges fit closely together like the tiles in a floor, hence it is also called pavement epithelium.
- The cells rest on a thin basement membrane.
e.g. This epithelium is present in the terminal bronchioles and alveoli of the lungs, wall of the Bowman' capsules and descending limbs of loops of henle of the nephrons of the kidneys, membranous labyrinth (internal ear), blood vessels, lympth vessels, heart, coelomic cavities, and rete testis of the testis.
- In the blood vessels, lymph vessels and heart it is called endothelium.
- In the coelom, it is called mesothelium.
- The cells of endothelium and mesothelium may become wavy, hence these epithelia are called 'tessellated'.
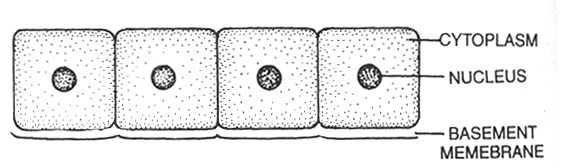
2. SIMPLE CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM -
- The cells are cubical and more or less squarish in shape.
- The nuclei are rounded and lie in the centre of the cells.
- The cells of cuboidal epithelium often form microvilli on their free surface.
- This given a brush-like appearance to their free border called brush bordered cuboidal epithelium.

eg. -
- Small salivary and pancreatic ducts, thyroid vesicles, parts of membranous labyrinth,
- Proximal and distal convoluted tubules of the nephrons and the pigment cell alyer of the retina of the eye.
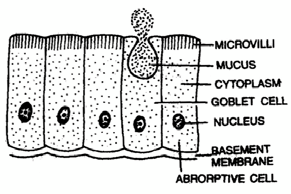
3. SIMPLE COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM -
- The cells are elongated and placed side by side like column.
- Certain cells of this epithelium contain mucus (a slimy substance) and are called goblet (or mucous) cells as they look like globlet.
e.g. The intestinal mucosa (= mucous membrane) has microvilli to increase the absorptive surface area and is called brush-bordered columnar epithelium which is highly absorptive.
- It lines the stomach, intestine, gall bladder and bile duct.
 It also forms the gastric glands, intestinal glands and pancreatic lobules (present in the pancreas) where it has secretory role and is called glandular epithelium.
It also forms the gastric glands, intestinal glands and pancreatic lobules (present in the pancreas) where it has secretory role and is called glandular epithelium.

Simple Columnar Epithelium Simple Ciliated Epithelium
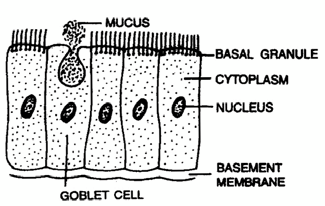
4. SIMPLE CILIATED EPITHELIUM -
- The cells bear numerous hair like outgrowths, the cilia, arising from basal granules. (i) Ciliated Columnar Epithelium -
- It comprises columnar cells which have cilia on the free surface.
e.g.
- This epithelium lines most of the respiratory tract and fallopian tubes (oviducts).
- It also lines the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord.
- It is also present in tympanic cavity and auditory tube (Eustachian tube).
(ii) Ciliated Cuboidal Epithelium -
- It consists of cubical cells which have cilia on the free surface. e.g. ® It occur in certain parts of nephorons of the kidneys.
- In the respiratory tract the cilia help to push mucus towards the pharynx (throat).
- In the oviducts the cilia help to move an egg towards the uterus.
- The cilia of the ventricles (cavities) of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord help to maintain the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid present there.
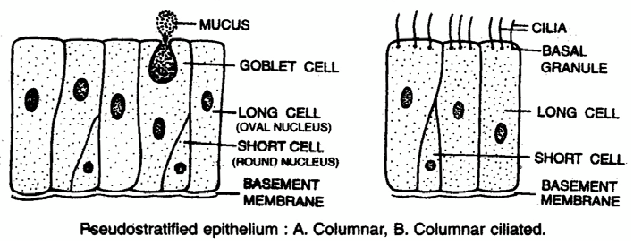
5. PSEUDO-STRATIFIED EPITHELIUM -
- Although epithelium is one cell thick yet it appears to be multi-layered which is due to the fact that the nuclei lie at different levels in different cells.
- The cells are columnar, but unequal in size.
- The long cells extend up to free surface.
- The short cells do not reach the outer free surface.
- The long cells have oval nuclei, however, short cels have rounded nuclei.
- Mucus secreting goblet cells also occur in this epithelium.