Q. Show the Structure of sulphuric acid?
Theoretical considerations require that the reaction be carried out at low temperature and high pressure. However, at low temperature, the reaction is too slow and high pressure makes the cost of plant uneconomical. The yields of S0, are optimised, by using a suitable catalyst, an excess of 02, and removing SO3, formed, the latter two shift the equilibrium to the right. Optimally the reaction is carried out at 700 - 725 R and one atmosphere pressure using vanadium pentoxide as catalyst and an excess of oxygen.
The purified SO2, is mixed with air (15) and is passed through a four stage catalytic converter operating between a range of temperatures, Fig. After conversion of SQ2 to SO3, to the extent of 99.5% or so, the gases come out of the converter.
Reaction of SO3 with HO2 is violent and gives a fog of dilute sulphuric acid. Therefore, SO3 is passed through concentrated H2S04 to give oleum. From oleum, H2S04 of any required concentration can be prepared by appropriately diluting it.
SO3 + H2SO4------------> H2S2O7 (oleum)
H2S2O7 + H2O----------> 2H2SO4
Concentrated sulphuric acid is a colourless, thick, oily liquid having sp.gr. 1.838 at 288 K,
m. p. 283.4 K and b .p. 613 K. At its boiling point, it gives dense white fumes of SO3. H2SO4, is a strong acid which is' almost completely ionised in aqueous solution. It behaves as adi basic acid, forming two distinct series of salts, namely, hydrogen sulphates, containing HSO: and sulphates, containing SO2-4. The dilute acid attacks many metals forming sulphates and hydrogen, but it does not react with lead, copper, mercury and silver.
Zn + H2SO4-----------------> ZnSO4 + H2
Concentrated H2, SO4, dissolves many metals giving sulphur dioxide. But there is no action on gold, platinum. Glass, silica and silicon-steel, the latter is used for making, distillation vessels.
Cu +2H2SO4---------------> CiSo4 + 2H2O + So2
Hot concentrated.H2S04 is a good oxidising agent. It oxidises H2, C, P, S, H1; HBr to H20, CO, H2PO3, SO2, I2 and Br2, respectively. It is also a good sulphonating agent.
C + H2SO4-----------------> CO + SO2+ H2O
C6H6 + H2SO4------------> C6H6 SO3H + H2 Benzene suphonic acid
Concentrated H2SO4 has a great affinity for water and is used a dehydrating agent. This property of concentrated sulphuric acid is used in drying gases like O2N2SO2 etc. H2SO4 chars organic substances by removing elements of water leaving black carbon behind e g.
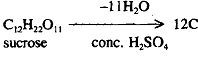
Below its melting point, anhydrous sulphuric acid is a white crystalline solid consisting of a throw-dimensional hydrogen-bonded network, which persists in the liquid state and makes the liquid viscous. The two hydroxyl groups and two oxygen's are tetrahedrally arranged around the S atom in H2S04, as shown in Fig. with S-OH and S-O bond lengths being 154 pm and 147 pm, respectively. This shortening of S-O bond shows p? d? bonding between sulphur and oxygen. The bond, as a result, has appreciable double bond character. In SO2-4 ion all the four S-0 bond lengths are 149 pm. This indicates extensive - delocalisation of bonding electrons.