Q. Show the chemical of Boron and aluminium?
Boron and aluminium when heated with nitrogen torn the nitrides BN and AIN Nitrides of Ga and in are formed by heating the elements with ammonia. Boron nitride can also be made by the action of ammonia on boron at 1300Kor by passing nitrogen over a mixture of boron trioxide and carbon at a slightly higher temperature:
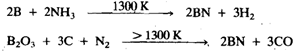
BN is isoelectronic with C2, and like carbon, it exists in diamond and graphite forms. The latter is a useful lubricant with additional advantage of being inert. Boron nitride is a white solid. It is chemically rather inert, but is hydrolysed to NH, and B3 (OH)3 by the action of steam or hot acids:
BN + 3H2O-----------------------------> B (OH)3+ NH3
Boron and aluminium on heating react with carbon to form the carbides B12C3, and Al4C3, respectively. Aluminium carbide is a colourless, high melting ionic solid and is decomposed by water to liberate methane. Therefore, it can be termed as aluminium methanide also:
Al4C3 + 12H20-------------------------------------> 4Al(OH)3 + 3CH4
On the other hand, the isolable form of boron carbide has the molecular composition B12C3. It is a black, extremely hard, high melting and chemically inert covalent compound. It is used as an abrasive for polishing and tool sharpening.
Boron on heating reacts with many metals to from binary compounds called borides, e.g., MgB2, VB and Fe2B, whereas other elements of Group 13 form alloys. Metal borides are extremely hard, chemically inert, non-volatile, refractory materials. They have high melting points and high thermal and electrical conductivities. The diborides of Ti, Zr, Hf, Nb and Ta all have melting points higher than 3200 K. The thermal and electrical conductivities of TiB2 and ZrB2, are about ten times greater than those of Ti and Zr metals.
Boron does not react with non-oxidising acids. Even hot concentrated oxidising acids react with boron only slowly to form boric acid:
2B + 3H2SO4 --- -----------------------> 2H3B03+ 3S02
B + 3HN03------------------------------> H3B03 + 3N02
Al, Ga, In and TI react with warm dilute HCI and H2S04 to replace hydrogen and form kf3+ except TI which forms TI+:
2M+ 6HCl------------------> 2M3+ 6Cl- + 3H2
2Tl+ 2HCl------------------> 2Tl+ + 2 Cl- + H2
With hot and conc. H2S04, SO, is liberated:
2M + 6H2S04----------------------------------> M2(S04), + 3S02 + 6H20
Hot and conc. HNO3, renders A1 and Ga passive. The initial attack of the acid covers the metal with an impervious, coherent, unreactive layer of oxide which prevents further attack. In and TI react with conc. HN03 to form metal trinitrates liberating NO2:
M + 6HN03 ---------------------> M(N03), + 3N02 + 3H20
Boron reacts with fused alkalies forming the borates:
2B + 6NaOH----------------------------------> 9 2Na3B03 + 3H2
Aluminium and gallimn dissolve in aqueous alkalis to form aluminate and gallate ions, respectively:
M + 4NaOH ----------------------------->+ NaM(OH)4 + 2H2
Thus, you see that the elements of Group 13 are fairly reactive and form many useful compounds such as hydrides, halides, nitrides, oxides, ox acids and their salts, etc. Let us now study some of the compounds of B and A1 in detail. Compounds of Ga, In and TI will be described only in brief, where appropriate, for the sake of comparison only.