Q. Show properties of the Borax?
Salts of boric acids are known as borates. As said earlier, hydrated borates occur naturally, e.g., borax, Na2B6011. 5H20, kernite, Na2 + 04H20. colemanite. Ca2B6011,.5H20, etc. Anhydrous borates can be made by fusion of boric acid and metal oxides.
Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, Na2B4+07+10H20, is commonly known as boric. It occurs in certain lakes in India, Tibet and U.S.A: It is obtained by extracting impure borax with water and concentrating the solution until crystals of borax separate out.
Borax can also be prepared from the mineral colemanite by boiling it with Na2CO3 solution:
Ca2B6O11+ 2Na2C03 -----------------------------------------------> Na2B407 + 2NaB02 + 2CaC03
Borax is crystallised from the filtrate after removing insoluble CaC03, By passing CO2, NaB02 present in the mother liquor is converted into borax:
4NaB02 + C02---------------------------> Na2B407 + Na2C03
Borax is a white crystalline solid. It is hydrolysed by water to give an alkaline solution:
Na2B4O7+ 7H2O-----------------> 4H3BO3+ 2NaOH
On heating, borax loses water to become anhydrous. Anhydrous borax on strong heating with NH4Cl gives boron nitride and boron trioxitde:
Na2B407 + 2NH4Cl ------------> 2BN'+ B2O3 + 2NaCl + 4H20
On heating alone, it decomposes to form NaBO2 and B203
Na2 B4O7------------------------> 2NaBO2+ B2O3
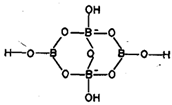
Borax possesses an anion [B4O5 (OH)4] 2- having both three and four coordinated boron as shown in fig. 6.8.