Equivalent Circuit of a Synchronous Machine
A review of the material about elementary synchronous machines is very helpful at this stage to recall the principles of operation for synchronous machines. To investigate the equivalent circuit of a synchronous machine, for the sake of simplicity, let us begin by considering an unsaturated cylindrical-rotor synchronousmachine. Effects of saliency and magnetic saturation can be considered later. Since for the present we are only concerned with the steady-state behavior of themachine, circuit parameters of the field and damperwindings need not be considered. The effect of the field winding, however, is taken care of by the flux produced by the dc field excitation and the ac voltage generated by the field flux in the armature circuit.
Thus, let ¯Ef be the ac voltage, known as excitation voltage, generated by the field flux. As for the armature winding, under balanced conditions of operation we will analyze it on a per-phase basis. The armature winding obviously has a resistance Ra and a leakage reactance Xl of the armature per phase.
The armature current ¯Ia produces the armature reaction flux, the effect of which can be represented by an inductive reactance Xφ, known as magnetizing reactance or armature reaction reactance. Thus Figure shows the equivalent circuits in phasor notation, with all per-phase quantities, for a cylindrical-rotor synchronous machine working as either a generator or a motor. The sum of the armature leakage reactance and the armature reaction reactance is known as the synchronous reactance,
Xs = Xφ + Xl
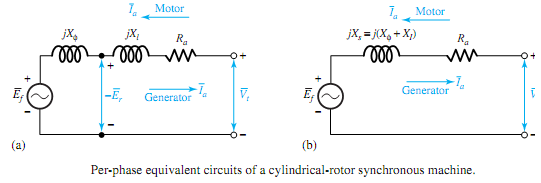
and Ra + jXs is called the synchronous impedance Zs. Thus, the equivalent circuit for an unsaturated cylindrical-rotor synchronous machine under balanced polyphase conditions reduces to that shown in Figure (b), in which the machine is represented on a per-phase basis by its excitation voltage ¯Ef in series with the synchronous impedance. Note that ¯Vt is the terminal per-phase rms voltage, usually taken as reference.