Sexual reproduction in Eukaryotes
In most eukaryotes, especially higher animals, individuals normally exhibit one or two sex phenotypes; female or male. In such species, females produce the female gametes-eggs, ovules or macrospores and males produce the male gamets -sperm, pollen or microsproes. Species with separation of sexes in different individuals are called dioecious or monosexual organisms. All higher organisms and some higher plants are dioecious. Species in which both male and female gametes are produced by each individual are called monoecious or bisexual organisms. In lower animals, the production of both eggs and sperms by the same organisms is more commonly called hermaphroditism, and individual organisms producing both the types of gametes are termed hermaphrodites.
Although the two sex phenotypes are usually quite easily distinguished in humans and fruit flies, it is not universally the case. In lower or the 'primitive' eukaryotes, the two sexes are phenotypically indistinguishable except for their reproductive organs. Indeed, in lower eukaryotes the two genetically distinct types of gametes are sometimes morphologically indistinguishable. This is called isogamy (iso meaning 'same'). Isogamy occurs in several simple eukaryotes, such as the green alga Chlamydomonas, fungi-Neurospora and protozoa-Paramecium. They may however, be identified by their sexual reproduction pattern.
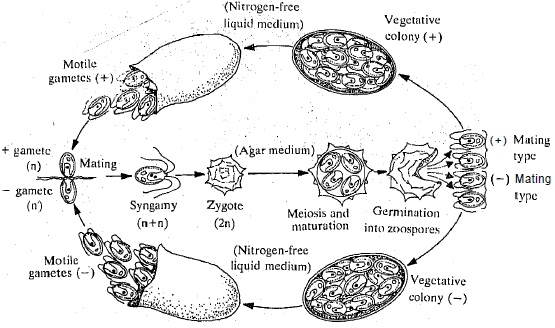
An individual belonging to one mating type exchanges genetic material by fusing only with an individual of another mating type but never with its own mating type. Therefore, the similar looking male and female gametes, or isogametes are actually physiologically different, as is evident by their mode of reproduction. Sexual differences between indi,viduals probably originated first in their gametes. Most of the plants are hermaphrodite, producing both types of gametes, but have various adaptations to promote cross fertilisation. One such adaptation is the phenomenon of self-sterility. Its examples are cheny and tobacco plant. Due to self sterility the plants have to undergo cross fertilisation, and the [esult is the recombination of genetic material.