Before searching at series solutions to a differential equation we will initially require to do a cursory review of power series. So, a power series is a series in the form,
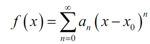 ........................(1)
........................(1)
Here, x0 and an are numbers. We can notice from that as a power series is a function of x. The function notation is not all the time contained, but sometimes this is so we place this in the definition above.
Before proceeding along with our review we must probably first recall just what series actually are. Recall that series are actually just summations. Then one method to write our power series is,
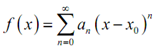
= a0 + a1 (x - x0) + a2 (x - x0)2 + a3 (x - x0)3+ .............. (2)
Notice finely that if we required to for some purpose we could all the time write the power series as,
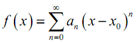
= a0 + a1 (x - x0) + a2 (x - x0)2 + a3 (x - x0)3+..............
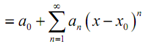
All which we're doing now there is noticing that if we avoid the first term (consequent to n = 0) the remains is just a series which starts at n = 1. While we do this we say which we've stripped out the n = 0, or first term. We don't require stopping at the first term either. If we strip out the initially three terms we'll find,
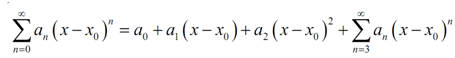
There are times while we'll need to do this so ensure that you can do it.
Here, as power series are functions of x and we know that not each series will actually exist, this then makes sense to ask if a power series will exist for all x. This question is answered by searching at the convergence of the power series. We say as a power series converges for x = c whether the series, converges.
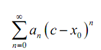
Recall here that series which will converge if the restrict of partial sums,
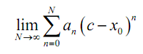
exists and it is finite. Conversely, a power series will converge for x=c if
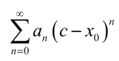
above is a finite number.
Remember that a power series will all the time converge if x = x0. During this case the power series will become ∞;
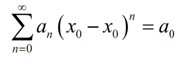
With this we here know that power series are guaranteed to exist for in any case one value of x. We have the subsequent fact regarding to the convergence of a power series.